Chinese Journal of Information Fusion
ISSN: 2998-3371 (Online) | ISSN: 2998-3363 (Print)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
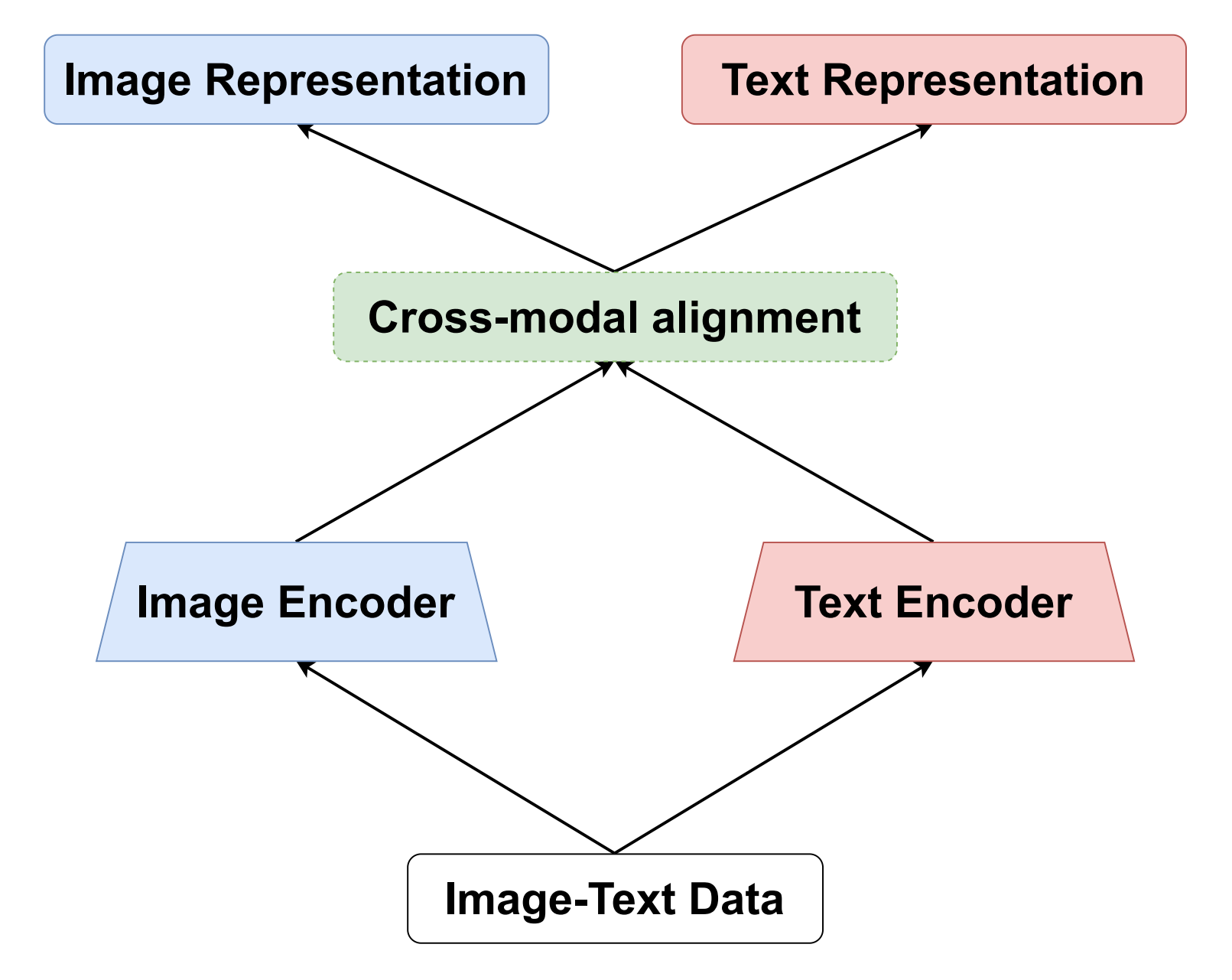
[1]Li, J., Li, D., Savarese, S., & Hoi, S. (2023, July). Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 19730-19742). PMLR.
[2]Zhang, P., Wang, X. D. B., Cao, Y., Xu, C., Ouyang, L., Zhao, Z., ... & Wang, J. (2023). Internlm-xcomposer: A vision-language large model for advanced text-image comprehension and composition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.15112.
[3]Zhu, H., Huang, J. H., Rudinac, S., & Kanoulas, E. (2024). Enhancing Interactive Image Retrieval With Query Rewriting Using Large Language Models and Vision Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.18746.
[4]Li, Y., Wang, W., Qu, L., Nie, L., Li, W., & Chua, T. S. (2024). Generative Cross-Modal Retrieval: Memorizing Images in Multimodal Language Models for Retrieval and Beyond. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.10805.
[5]Levy, M., Ben-Ari, R., Darshan, N., & Lischinski, D. (2024). Chatting makes perfect: Chat-based image retrieval. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36.
[6]Karthik, S., Roth, K., Mancini, M., & Akata, Z. (2023). Vision-by-language for training-free compositional image retrieval. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.09291.
[7]Team, G., Anil, R., Borgeaud, S., Wu, Y., Alayrac, J. B., Yu, J., ... & Ahn, J. (2023). Gemini: a family of highly capable multimodal models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.11805.
[8]Kim, W., Son, B., & Kim, I. (2021, July). Vilt: Vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 5583-5594). PMLR.
[9]Li, G., Duan, N., Fang, Y., Gong, M., & Jiang, D. (2020, April). Unicoder-vl: A universal encoder for vision and language by cross-modal pre-training. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (Vol. 34, No. 07, pp. 11336-11344).
[10]Li, L. H., Yatskar, M., Yin, D., Hsieh, C. J., & Chang, K. W. (2019). Visualbert: A simple and performant baseline for vision and language. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.03557.
[11]Lu, J., Batra, D., Parikh, D., & Lee, S. (2019). Vilbert: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. Advances in neural information processing systems, 32.
[12]Radford, A., Kim, J. W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., ... & Sutskever, I. (2021, July). Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 8748-8763). PMLR.
[13]Kim, D., Kim, N., & Kwak, S. (2023). Improving cross-modal retrieval with set of diverse embeddings. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 23422-23431).
[14]Jia, C., Yang, Y., Xia, Y., Chen, Y. T., Parekh, Z., Pham, H., ... & Duerig, T. (2021, July). Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 4904-4916). PMLR.
[15]Wang, B., Yang, Y., Xu, X., Hanjalic, A., & Shen, H. T. (2017, October). Adversarial cross-modal retrieval. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 154-162).
[16]Zhen, L., Hu, P., Wang, X., & Peng, D. (2019). Deep supervised cross-modal retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 10394-10403).
[17]Tang, X., Wang, Y., Ma, J., Zhang, X., Liu, F., & Jiao, L. (2023). Interacting-Enhancing Feature Transformer for Cross-modal Remote Sensing Image and Text Retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
[18]Lu, H., Fei, N., Huo, Y., Gao, Y., Lu, Z., & Wen, J. R. (2022). Cots: Collaborative two-stream vision-language pre-training model for cross-modal retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer Vision and pattern recognition (pp. 15692-15701).
[19]Xie, C. W., Wu, J., Zheng, Y., Pan, P., & Hua, X. S. (2022, October). Token embeddings alignment for cross-modal retrieval. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (pp. 4555-4563).
[20]Jiang, Q. Y., & Li, W. J. (2017). Deep cross-modal hashing. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3232-3240).
[21]Wu, G., Lin, Z., Han, J., Liu, L., Ding, G., Zhang, B., & Shen, J. (2018, July). Unsupervised Deep Hashing via Binary Latent Factor Models for Large-scale Cross-modal Retrieval. In IJCAI (Vol. 1, No. 3, p. 5).
[22]Li, C., Deng, C., Li, N., Liu, W., Gao, X., & Tao, D. (2018). Self-supervised adversarial hashing networks for cross-modal retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4242-4251).
[23]Li, T., Yang, X., Wang, B., Xi, C., Zheng, H., & Zhou, X. (2022, June). Bi-CMR: bidirectional reinforcement guided hashing for effective cross-modal retrieval. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 36, No. 9, pp. 10275-10282).
[24]Tu, J., Liu, X., Lin, Z., Hong, R., & Wang, M. (2022, October). Differentiable cross-modal hashing via multimodal transformers. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (pp. 453-461).
[25]Rasiwasia, N., Costa Pereira, J., Coviello, E., Doyle, G., Lanckriet, G. R., Levy, R., & Vasconcelos, N. (2010, October). A new approach to cross-modal multimedia retrieval. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 251-260).
[26]Chua, T. S., Tang, J., Hong, R., Li, H., Luo, Z., & Zheng, Y. (2009, July). Nus-wide: a real-world web image database from national university of singapore. In Proceedings of the ACM international conference on image and video retrieval (pp. 1-9).
[27]Escalante, H. J., Hernández, C. A., Gonzalez, J. A., López-López, A., Montes, M., Morales, E. F., ... & Grubinger, M. (2010). The segmented and annotated IAPR TC-12 benchmark. Computer vision and image understanding, 114(4), 419-428.
[28]Huiskes, M. J., & Lew, M. S. (2008, October). The mir flickr retrieval evaluation. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM international conference on Multimedia information retrieval (pp. 39-43).
[29]Rashtchian, C., Young, P., Hodosh, M., & Hockenmaier, J. (2010, June). Collecting image annotations using amazon’s mechanical turk. In Proceedings of the NAACL HLT 2010 workshop on creating speech and language data with Amazon’s Mechanical Turk (pp. 139-147).
[30]Lin, T. Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., ... & Zitnick, C. L. (2014). Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part V 13 (pp. 740-755). Springer International Publishing.
[31]Tan, W., Zhu, L., Li, J., Zhang, H., & Han, J. (2022). Teacher-student learning: Efficient hierarchical message aggregation hashing for cross-modal retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia.
[32]Peng, Y., & Qi, J. (2019). CM-GANs: Cross-modal generative adversarial networks for common representation learning. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 15(1), 1-24.
[33]Dong, X., Liu, L., Zhu, L., Nie, L., & Zhang, H. (2021). Adversarial graph convolutional network for cross-modal retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 32(3), 1634-1645.
[34]Zeng, Z., & Mao, W. (2022). A comprehensive empirical study of vision-language pre-trained model for supervised cross-modal retrieval. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.02772.
[35]Tu, R. C., Mao, X. L., Ma, B., Hu, Y., Yan, T., Wei, W., & Huang, H. (2020). Deep cross-modal hashing with hashing functions and unified hash codes jointly learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 34(2), 560-572.
[36]Huo, Y., Qin, Q., Dai, J., Wang, L., Zhang, W., Huang, L., & Wang, C. (2023). Deep semantic-aware proxy hashing for multi-label cross-modal retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology.
[37]Zhu, L., Wang, T., Li, F., Li, J., Zhang, Z., & Shen, H. T. (2023). Cross-Modal Retrieval: A Systematic Review of Methods and Future Directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.14263.
[38]Zhou, K., Hassan, F. H., & Hoon, G. K. (2023). The State of the Art for Cross-Modal Retrieval: A Survey. IEEE Access.
[39]Wang, X., Li, L., Li, Z., Wang, X., Zhu, X., Wang, C., ... & Xiao, Y. (2023, February). AGREE: aligning cross-modal entities for image-text retrieval upon vision-language pre-trained models. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (pp. 456-464).
Chinese Journal of Information Fusion
ISSN: 2998-3371 (Online) | ISSN: 2998-3363 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/iece/