Abstract
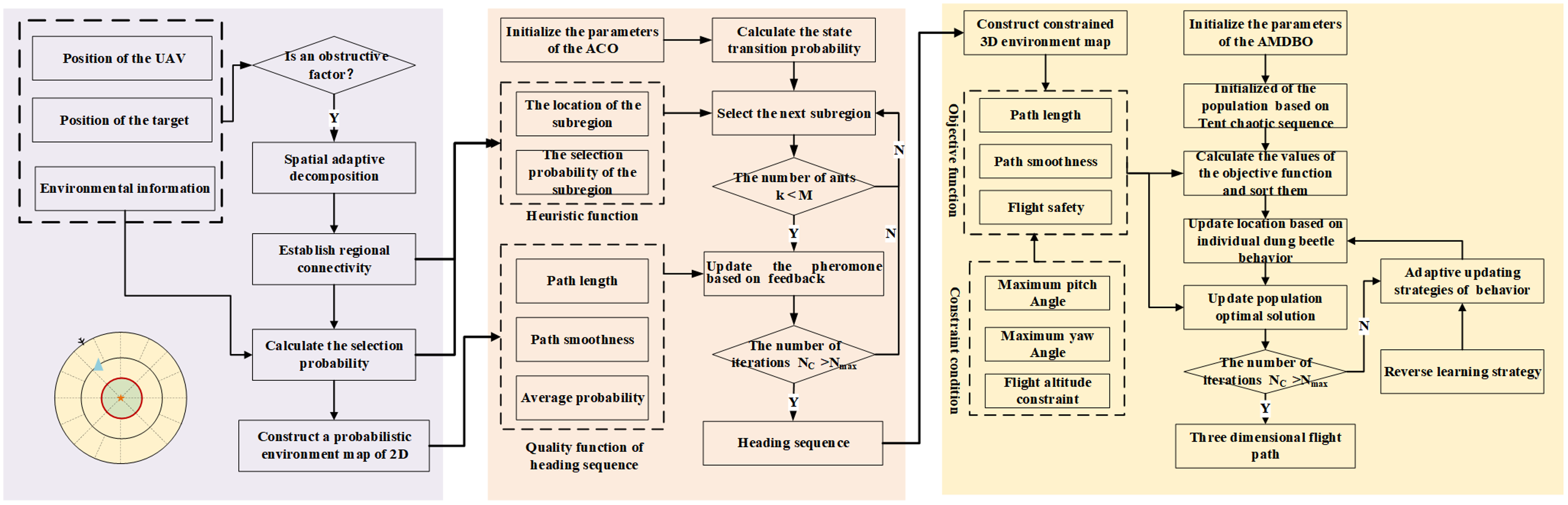
In response to the challenges associated with the inefficiency and poor quality of 3D path planning for Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) operating in vast airspace, a novel two-layer path planning method is proposed based on a divide-and-conquer methodology. This method segregates the solution process into two distinct stages: heading planning and path planning, thereby ensuring the planning of both efficiency and path quality. Firstly, the path planning phase is formulated as a multi-objective optimization problem, taking into account the environmental constraints of the UAV mission and path safety. Subsequently, the multi-dimensional environmental data is transformed into a two-dimensional probabilistic map. An improved ant colony algorithm is proposed to efficiently generate high-quality sets of headings, facilitating the preliminary heading planning for UAVs. Then, the three-dimensional environment of the heading regions is extracted, and an improved Dung Beetle algorithm with multiple strategies is proposed to optimize the three-dimensional path in the secondary layer accurately. The efficacy and quality of the proposed path planning methodology are substantiated through comprehensive simulation analysis.
Keywords
two-dimensional probabilistic map
trajectory planning
optimization algorithm
two-Layer path planning
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants (61972363 and 61672472).
Cite This Article
APA Style
Yang, T. & Yang, F. (2024). A High-Efficiency Two-Layer Path Planning Method for UAVs in Vast airspace. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion, 1(2), 109–125. https://doi.org/10.62762/CJIF.2024.596648
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue