Abstract
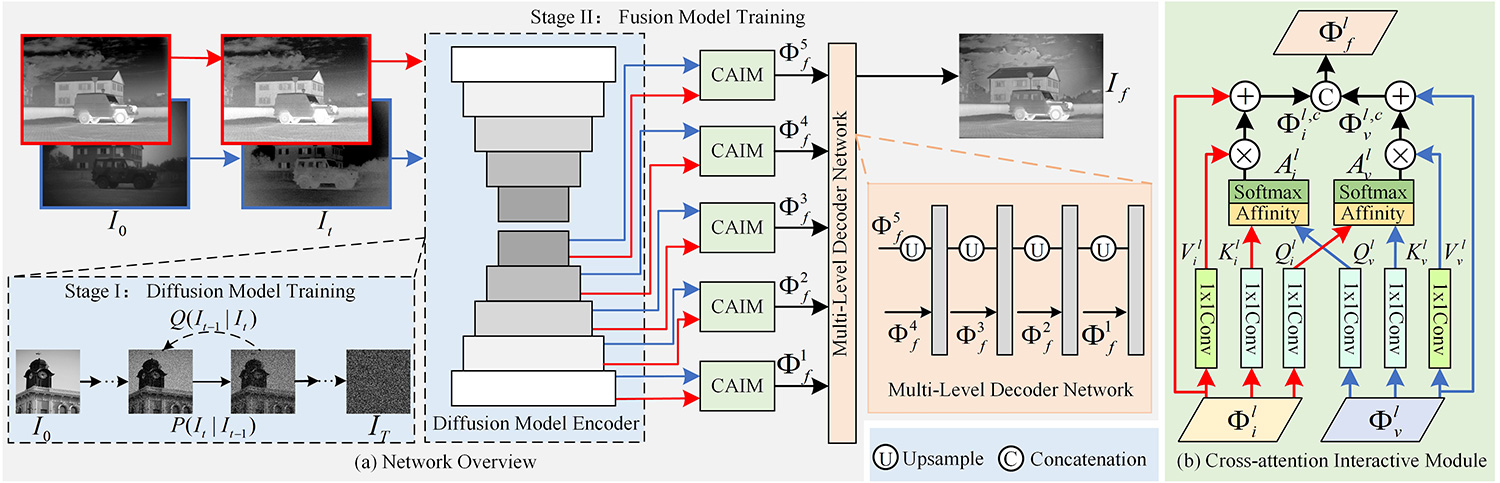
Image fusion aims to integrate complementary information from different sensors into a single fused output for superior visual description and scene understanding. The existing GAN-based fusion methods generally suffer from multiple challenges, such as unexplainable mechanism, unstable training, and mode collapse, which may affect the fusion quality. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces a diffusion model guided cross-attention learning network, termed as DMFuse, for infrared and visible image fusion. Firstly, to improve the diffusion inference efficiency, we compress the quadruple channels of the denoising UNet network to achieve more efficient and robust model for fusion tasks. After that, we employ the pre-trained diffusion model as an autoencoder and incorporate its strong generative priors to further train the following fusion network. This design allows the generated diffusion features to effectively showcase high-quality distribution mapping ability. In addition, we devise a cross-attention interactive fusion module to establish the long-range dependencies from local diffusion features. This module integrates the global interactions to improve the complementary characteristics of different modalities. Finally, we propose a multi-level decoder network to reconstruct the fused output. Extensive experiments on fusion tasks and downstream applications, including object detection and semantic segmentation, indicate that the proposed model yields promising performance while maintaining competitive computational efficiency. The code and data are available at https://github.com/Zhishe-Wang/DMFuse.
Data Availability Statement
The code and data supporting this study are publicly available on GitHub at the following link: https://github.com/Zhishe-Wang/DMFuse.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province under Grant 202203021221144, and the Patent Transformation Program of Shanxi Province under Grant 202405012.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Qi, W., Zhang, Z., & Wang, Z. (2024). DMFuse: Diffusion Model Guided Cross-Attention Learning for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion, 1(3), 226–242. https://doi.org/10.62762/CJIF.2024.655617
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2024 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2024 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2024 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 