Abstract
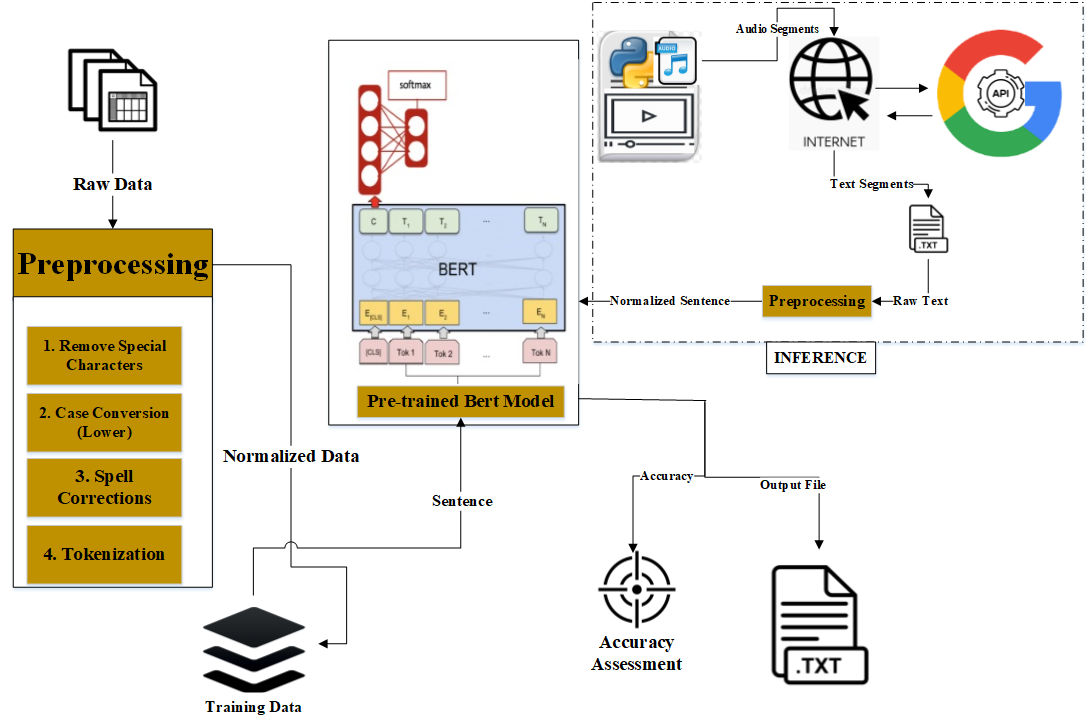
social media has significantly transformed the digital landscape by enabling an unprecedented expansion of content, further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which increased the demand for online classes, virtual meetings, and recorded conferences. While major technology companies have previously employed sentiment analysis and opinion mining to gauge user feedback, this study proposes a novel framework for emotion-based video content analysis. The proposed method extracts audio from social media videos and applies Speech-to-Text (STT) conversion. The extracted text is then processed using a pre-trained BERT model, leveraging its fine-tuned capabilities and 110 million parameters to enhance emotion recognition. To improve inference, we modify the initial embedding layers of BERT to refine emotional analysis for unseen video content, ensuring better alignment with viewers' emotional responses. Experimental results demonstrate that the pre-trained BERT model outperforms traditional deep learning and machine learning approaches, achieving 83% accuracy and an F1 score of 83. Comparatively, CNN and LSTM models achieved 74% and 73% accuracy, respectively, while SVM resulted in 72% accuracy. The proposed framework offers a more refined emotional analysis, potentially improving user engagement by making content more relatable and emotionally intuitive for viewers.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Akbar, Z., Ghani, M. U., & Aziz, U. (2025). Boosting Viewer Experience with Emotion-Driven Video Analysis: A BERT-based Framework for Social Media Content. Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Bioinformatics, 1(1), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.62762/JAIB.2025.954751
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 