Abstract
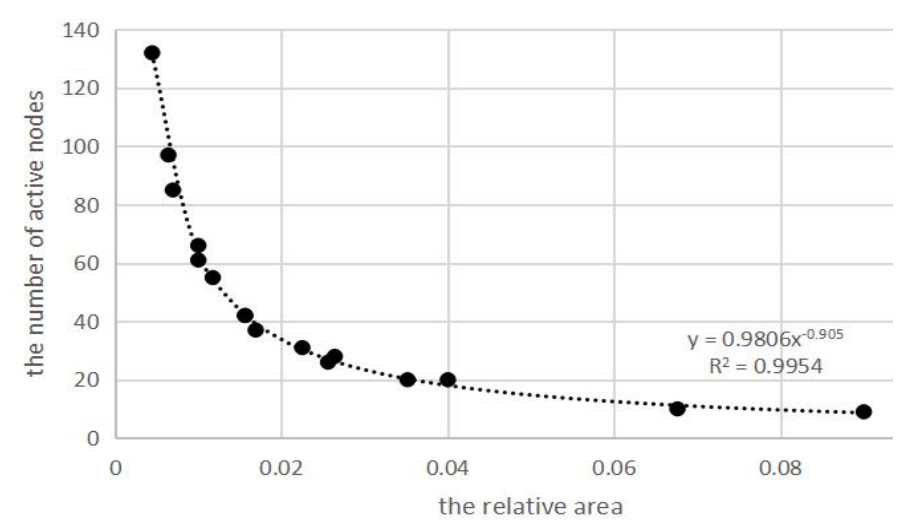
In order to optimize the deployment of wireless sensor network nodes, and avoid network energy consumption increase due to node redundancy and uneven coverage, the multi-objective mathematical optimization problem of area coverage is transformed into a function problem. Aiming at network coverage rate, node dormancy rate and network coverage uniformity, the idea of genetic algorithm mutation is introduced based on the discrete binary particle swarm optimization and the global optimal speed is mutated to avoid the algorithm falling into the local optimal solution. In order to further improve the optimization ability of the algorithm, the adaptive learning factor and inertia weight are introduced to obtain the optimal deployment algorithm of wireless sensor network nodes. The experimental results show that the algorithm can reduce the number of active nodes efficiently, improve coverage uniformity, reduce network energy consumption and prolong network lifetime under the premise that the coverage rate is greater than 90%, and compared with an algorithm called coverage configuration protocol, an algorithm called finding the minimum working sets in wireless sensor networks, and an algorithm called binary particle swarm optimization-g in literature, the number of active nodes in this algorithm is reduced by about 36%, 30% and 23% respectively.
Keywords
Uniform coverage
discrete binary particle swarm optimization algorithm
wireless sensor network
optimal deployment
Cite This Article
APA Style
Li, Y., & Cao, J. (2023). Adaptive Binary Particle Swarm Optimization for WSN Node Optimal Deployment Algorithm. IECE Transactions on Internet of Things, 1(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIOT.2023.564457
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue