Abstract
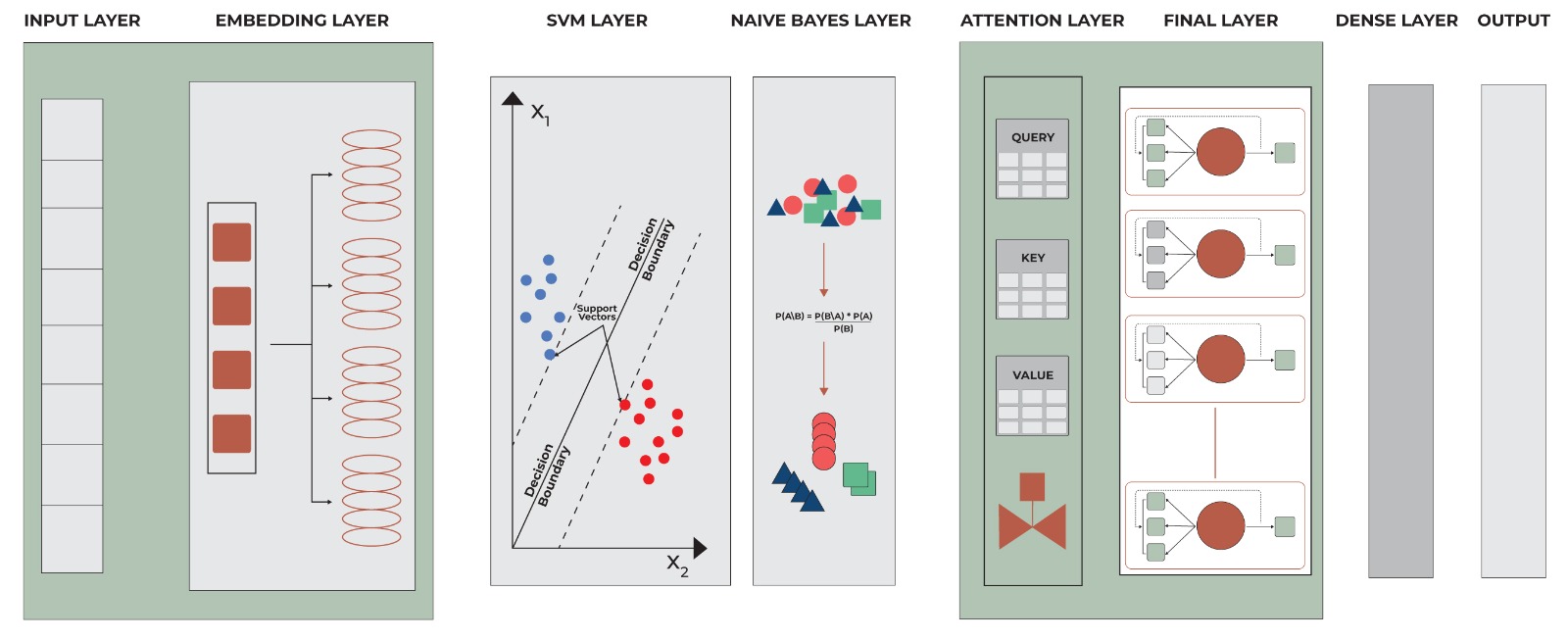
The increasing prevalence of fake news on social media has become a significant challenge in today’s digital landscape. This paper proposes a hybrid framework for fake news detection, combining Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques and machine learning algorithms. Using Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) for feature extraction, and classifiers such as Logistic Regression (LR), Naïve Bayes (NB), and Support Vector Machines (SVM), the model integrates Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) with Logistic Regression to achieve 95% accuracy and 93% precision on a Kaggle dataset. The results highlight the potential of combining statistical and NLP approaches to improve fake news detection accuracy.
Keywords
fake news
natural language processing
statistical technique
machine learning
maximum likelihood estimation
social media
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Nadeem, M., Abbas, P., Zhang, W., Rafique, S., & Iqbal, S. (2024). Enhancing Fake News Detection with a Hybrid NLP-Machine Learning Framework. IECE Transactions on Intelligent Systematics, 1(3), 203–214. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIS.2024.461943
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue