Abstract
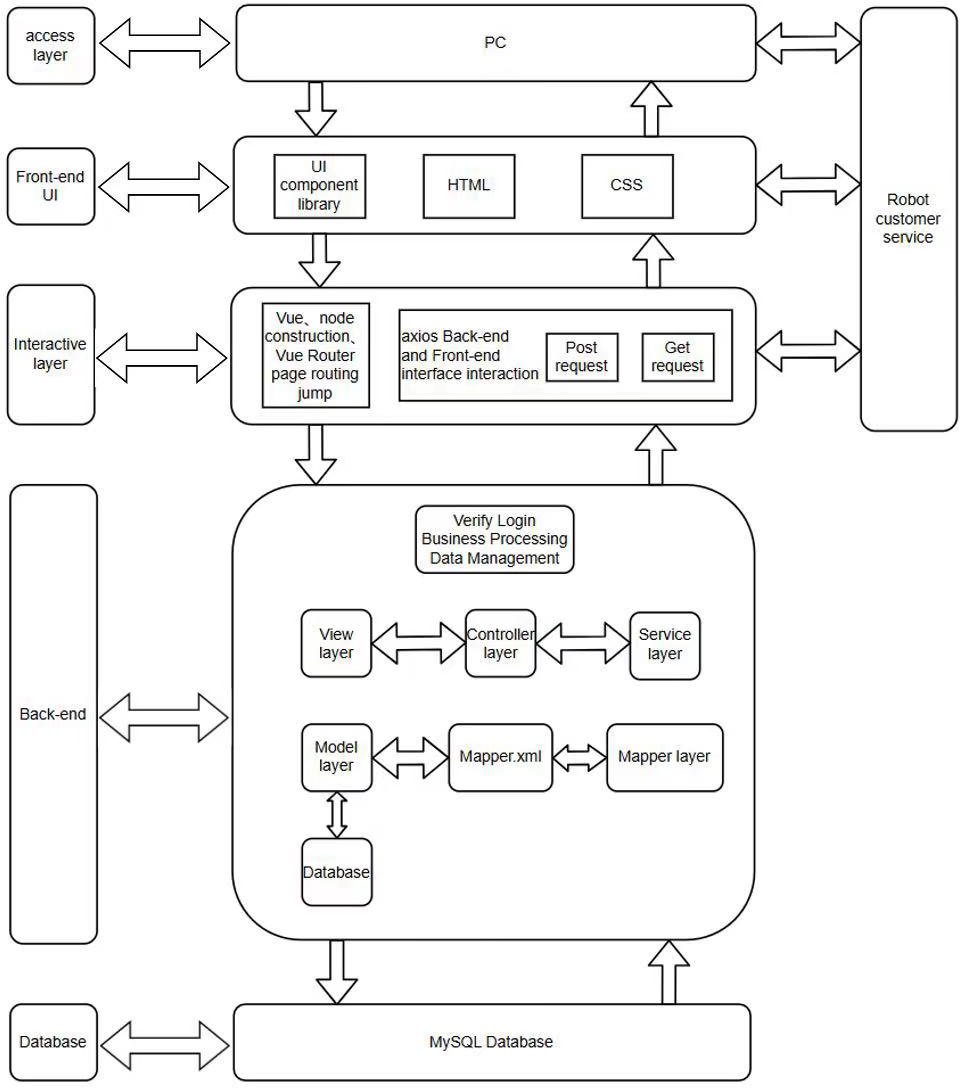
With the rapid development of e-commerce, consumers encounter more and more frequent customer service problems in the shopping process, especially during peak periods, the burden of manual customer service is heavy, and it is difficult to provide timely and effective service. In addition, enterprises are faced with high labor costs and low service efficiency. However, existing customer service systems are still deficient in user experience and intelligence level. In order to solve these problems, I designed a mall system and integrated Google's Dialogflow robot service in it, which realizes intelligent customer service functions through natural language processing technology to help users get real-time and accurate responses during the shopping process. This system can significantly improve the customer experience and reduce the customer service cost of enterprises, and has a wide range of application prospects.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Zhang, K., Wang, X., & Wang, Y. (2024). Dialogflow-based Robot Customer Service in Online Shopping Malls. IECE Transactions on Intelligent Unmanned Systems, 1(2), 55–62. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIUS.2024.257761
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue