Abstract
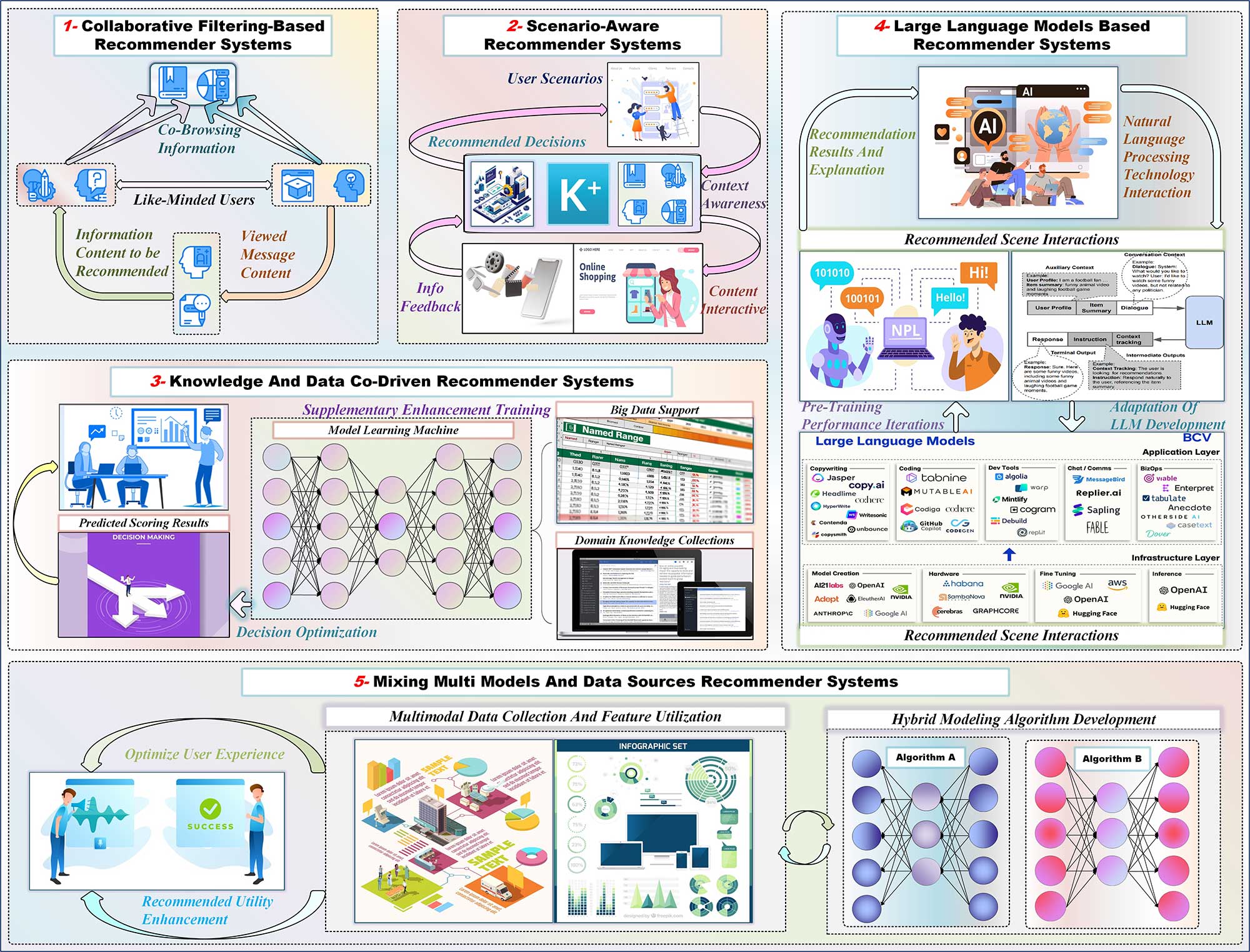
The proliferation of Recommender Systems (RecSys), driven by their expanding application domains, explosive data growth, and exponential advancements in computing capabilities, has cultivated a dynamic and evolving research landscape. This paper comprehensively reviews the foundational concepts, methodologies, and challenges associated with RecSys from technological and social scientific lenses. Initially, it categorizes personalized RecSys technical solutions into five paradigms: collaborative filtering, scenario-aware, knowledge & data co-driven approaches, large language models, and hybrid models integrating diverse data sources. Subsequently, the paper analyses the key challenges and future trajectories in five technical domains: general technologies, recommendation accuracy, cold-start problems, explainability, and privacy protection.
The review also explores the intersection between RecSys and social sciences, emphasizing how RecSys is shaped by and, in turn, shapes social structures, cultural norms, and societal biases, alongside its influence on decision-making, behaviour, and identity formation. Identified research gaps highlight the need for deeper investigations into cross-cultural variations and long-term effects, as well as for integrating sociological and psychological insights with technical designs. This review systematically encapsulates the current research landscape of RecSys across technological and sociological domains, thereby guiding researchers toward identifying potential advancements and future research directions.
Keywords
recommender system
personalized recommendation
technological roadmap
sociological intersections
psychological implications
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Cite This Article
APA Style
An, Y., Tan, Y., Sun, X., & Ferrari, G. (2024). Recommender System: A Comprehensive Overview of Technical Challenges and Social Implications. IECE Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control, 1(1), 30–51. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSCC.2024.898503
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
IECE or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue