Abstract
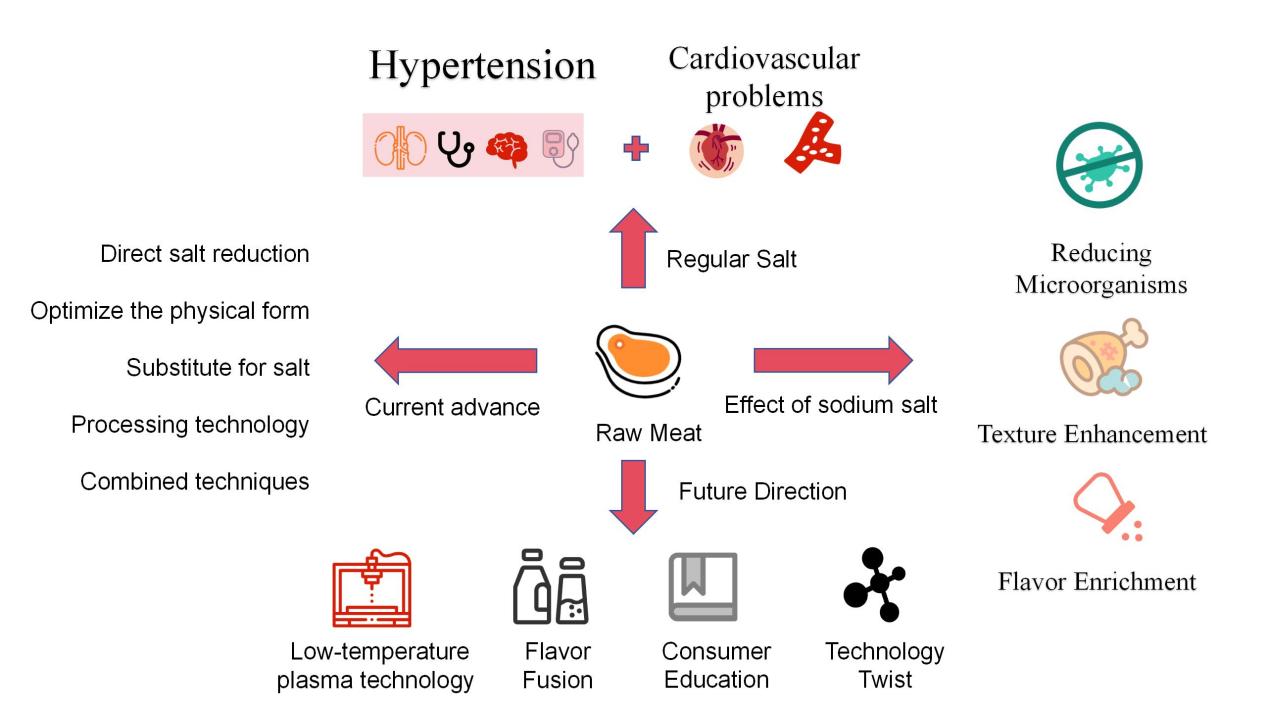
The paper discusses the multiple functions of salt in meat products, such as enhancing flavor, adjusting texture, reducing water activity, inhibiting bacteria, and extending shelf life. It also emphasizes the global health concern of excessive sodium intake and the necessity of reducing salt in processed meats to address this issue. Additionally, this paper presents the importance of reducing microorganisms in meat products through the use of sodium chloride and additives like sodium nitrite to ensure product safety. Furthermore, it highlights the strategy of changing the physical structure of salt to reduce salt content without compromising product quality, such as using 3D printing technology to control salt distribution on the food surface and micronization technology to enhance saltiness while reducing salt usage.
Keywords
meat product processing
salt reduction
sodium chloride
non-sodium salt substitution
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Zou, T. (2024). Salt Reduction in Processed Meats: Current Advances and Future Directions. Agricultural Science and Food Processing, 1(1), 4–20. https://doi.org/10.62762/ASFP.2024.261094
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue