Abstract
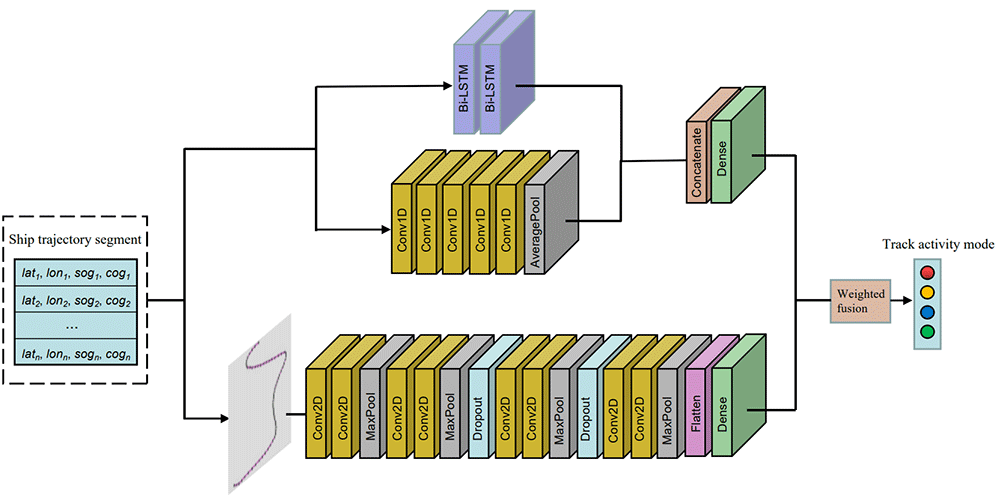
The unrestricted development and utilization of marine resources have resulted in a series of practical problems, such as the destruction of marine ecology. The wide application of radar, satellites and other detection equipment has gradually led to a large variety of large-capacity marine spatiotemporal trajectory data from a vast number of sources. In the field of marine domain awareness, there is an urgent need to use relevant information technology means to control and monitor ships and accurately classify and identify ship behavior patterns through multisource data fusion analysis. In addition, the increase in the type and quantity of trajectory data has produced a corresponding increase in the complexity and difficulty of data processing that cannot be adequately addressed by traditional data mining algorithms. Therefore, this paper provides a deep learning-based algorithm for the recognition of four main motion types of the ship from automatic identification system (AIS) data: anchoring, mooring, sailing and fishing. A new method for classifying patterns is presented that combines the computer vision and time series domains. Experiments are carried out on a dataset constructed from the open AIS data of ships in the coastal waters of the United States, which show that the method proposed in this paper achieves more than 95\% recognition accuracy. The experimental results confirm that the method proposed in this paper is effective in classifying ship trajectories using AIS data and that it can provide efficient technical support for marine supervision departments.
Keywords
Deep learning
Trajectory Xlassification
AIS Data
Data Fusion
Ship Monitoring
Funding
This work was supported by the key research and development program of Zhejiang Province (2019C05005).
Cite This Article
APA Style
Liu, J., Chen, Z., Zhou, J., Xue, A., Peng, D., Gu, Y., & Chen, H. (2024). Research on A Ship Trajectory Classification Method Based on Deep Learning. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion, 1(1), 3–15. https://doi.org/10.62762/CJIF.2024.361873
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue