Abstract
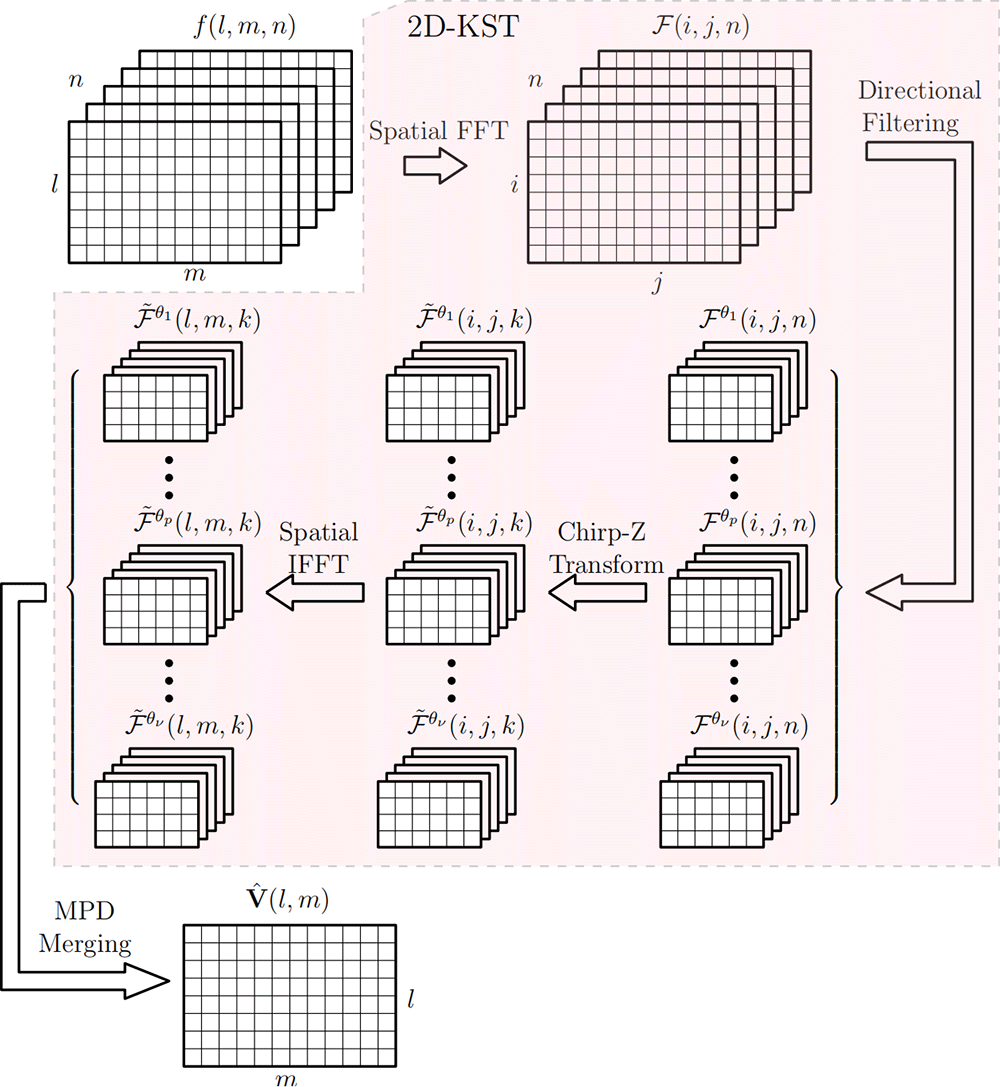
Considering the tractability of OGM (Occupancy Grid Map) and its wide use in the dynamic environment representation of mobile robotics, the extraction of motion information from successive OGMs are very important for many tasks, such as SLAM (Simultaneously Localization And Mapping) and DATMO (Detection and Tracking of Moving Object). In this paper, we propose a novel motion extraction method based on the signal transform, called as S-KST (Spatial Keystone Transform), for the motion detection and estimation from successive noisy OGMs. It extends the KST in radar imaging or motion compensation to 1D spatial case (1DS-KST) and 2D spatial case (2DS-KST) combined multiple hypotheses about possible directions of moving obstacles. Meanwhile, the fast algorithm of 2DS-KST based on Chirp Z-Transform (CZT) is also given, which includes five steps, i.e. spatial FFT, directional filtering, CZT, spatial IFFT and Maximal Power Detector (MPD) merging and its computational complexity is proportional to the 2D-FFT. Simulation test results for the point objects and the extended objects show that SKST has a good performance on the extraction of sub-pixel motions in very noisy environment, especially for those slowly moving obstacles.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62303478), ATR Foundation (2035250204) and Key Lab. Foundation (220302).
Cite This Article
APA Style
Fan, H., Lu, D., Jiang, Y., & Lilienthal, A. J. (2024). Extraction of Motion Information from Occupancy Grid Map Using Keystone Transform. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion, 1(1), 63–78. https://doi.org/10.62762/CJIF.2024.361892
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue