Abstract
In recent years, the field of electroencephalography (EEG) analysis has witnessed remarkable advancements, driven by the integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence. This survey aims to encapsulate the latest developments, focusing on emerging methods and technologies that are poised to transform our comprehension and interpretation of brain activity. The structure of this paper is organized according to the categorization within the machine learning community, with representation learning as the foundational concept that encompasses both discriminative and generative approaches. We delve into self-supervised learning methods that enable the robust representation of brain signals, which are fundamental for a variety of downstream applications. Within the realm of discriminative methods, we explore advanced techniques such as graph neural networks (GNN), foundation models, and approaches based on large language models (LLMs). On the generative front, we examine technologies that leverage EEG data to produce images or text, offering novel perspectives on brain activity visualization and interpretation. This survey provides an extensive overview of these cutting-edge techniques, their current applications, and the profound implications they hold for future research and clinical practice. The relevant literature and open-source materials have been compiled and are consistently updated at https://github.com/wpf535236337/LLMs4TS.
Keywords
electroencephalography (EEG)
self-supervised learning (SSL)
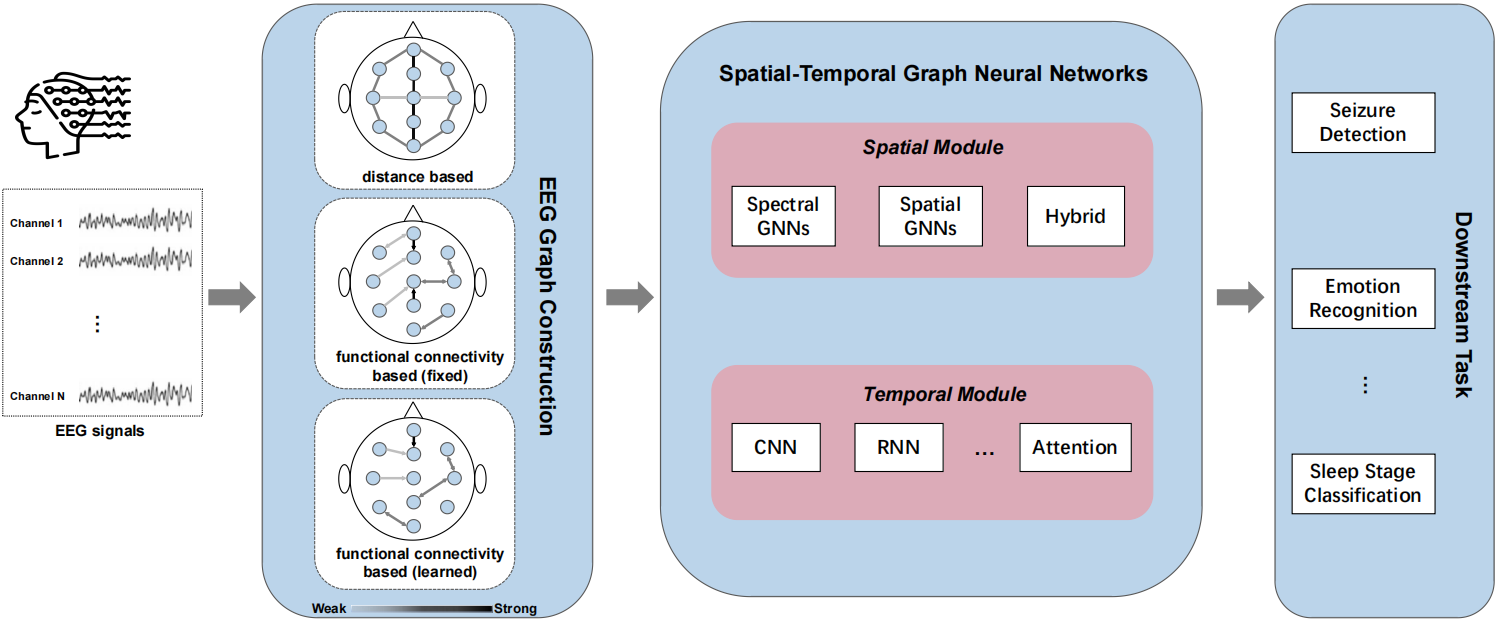
graph neural networks (GNN)
foundation models
large language models (LLMs)
generative models
Funding
This work was supported by NSFC under grant 62136002 and 62477014, Ministry of Education Research Joint Fund Project under grant 8091B042239, and Shanghai Trusted Industry Internet Software Collaborative Innovation Center.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Wang, P., Zheng, H., Dai, S., Wang, Y., Gu, X., Wu, Y, & Wang, X. (2024). A Comprehensive Survey on Emerging Techniques and Technologies in Spatio-Temporal EEG Data Analysis. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion, 1(3), 183–211. https://doi.org/10.62762/CJIF.2024.876830
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue