Abstract
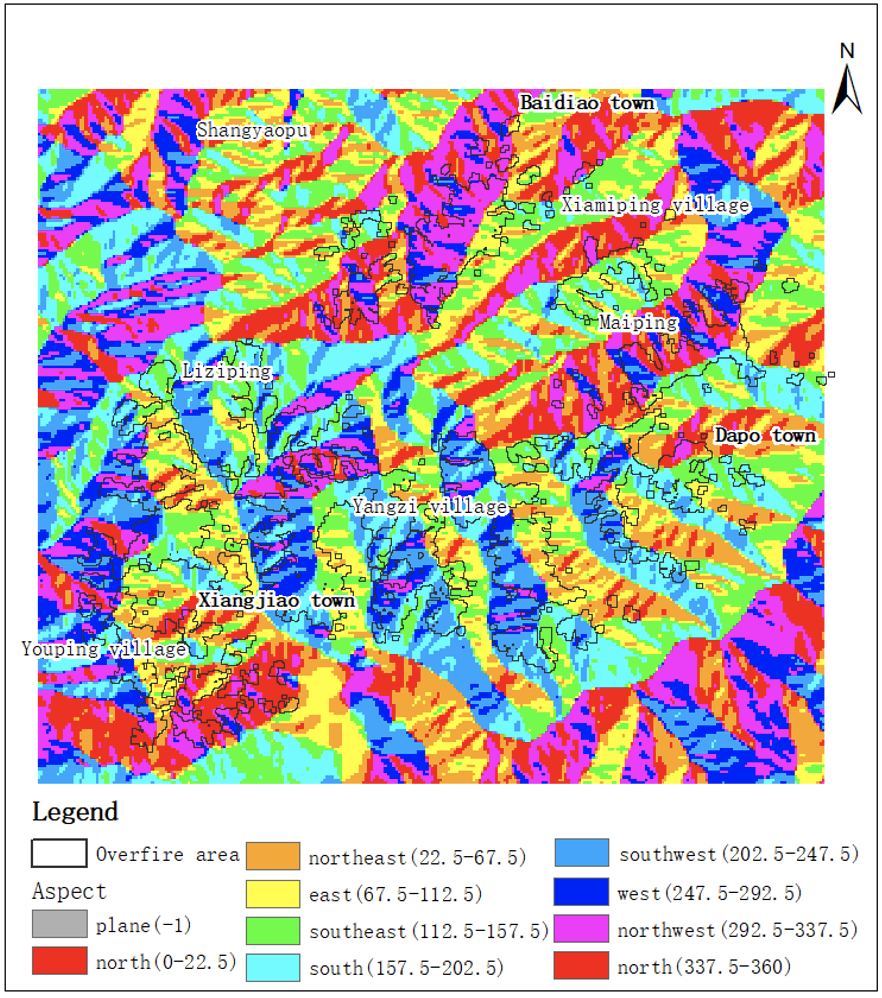
Because of the special geographical location, dry weather, high temperature and dense vegetation in Liangshan, Sichuan, it is easy to cause forest fires, so it is of great significance to use remote sensing data to evaluate forest fires in Liangshan, Sichuan. In this paper, the forest fire in Muli County, Liangshan, Sichuan Province on March 28th, 2020 was evaluated by using Landsat-8 remote sensing data which can be obtained free of charge. The NDVI of the pre-processed remote sensing images before and after the fire was calculated respectively. After the difference was made, the threshold of the classification of fire and non-fire areas was determined according to the maximum inter-class difference threshold method, and then the over-fire areas were extracted, and the interference was eliminated by open operation. And using the DEM data of the study area, combined with the topography of the study area, the over-fire area is analyzed. The results show that the "3.28" forest fire in Muli County, Sichuan Province, which is studied, belongs to a serious forest fire according to the burned area.
Keywords
Forest fire
Remote sensing assessment
NDVI
Cite This Article
APA Style
Y. Hua & X. Wang (2023). Forest Fire Assessment and Analysisin Liangshan, Sichuan Province Based on Remote Sensing.IECE Transactions on Internet of Things, 1(1), 15–21. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIOT.2023.862892
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue