Abstract
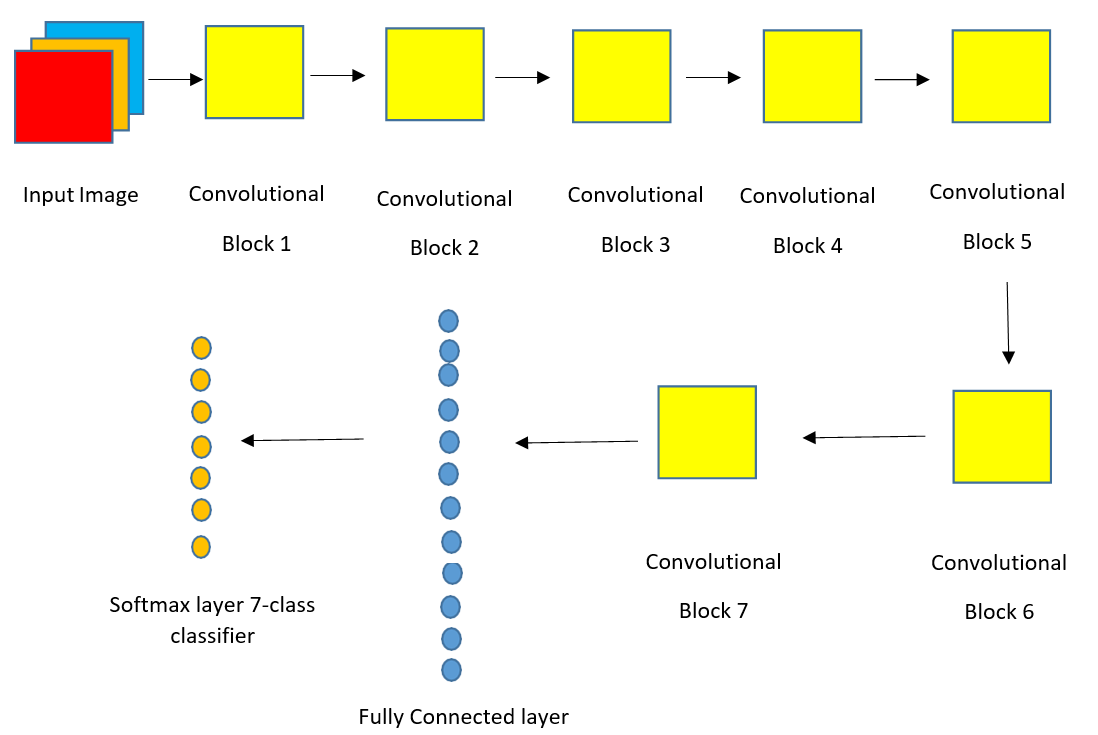
Indoor scene recognition poses considerable hurdles, especially in cluttered and visually analogous settings. Although several current recognition systems perform well in outside settings, there is a distinct necessity for enhanced precision in inside scene detection, particularly for robotics and automation applications. This research presents a revolutionary deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model tailored with bespoke parameters to improve indoor picture comprehension. Our proprietary dataset consists of seven unique interior scene types, and our deep CNN model is trained to attain excellent accuracy in classification tasks. The model exhibited exceptional performance, achieving a training accuracy of 99%, a testing accuracy of 89.73%, a precision of 90.11%, a recall of 89.73%, and an F1-score of 89.79%. These findings underscore the efficacy of our methodology in tackling the intricacies of indoor scene recognition. This research substantially advances the domain of robotics and automation by establishing a more resilient and dependable framework for autonomous navigation and scene comprehension in GPS-denied settings, facilitating the development of more efficient and intelligent robotic systems.
Keywords
indoor scene recognition
deep convolutional neural network (CNN)
robotics and automation autonomous navigation and GPS-Denied environments
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the Data and Intelligence Laboratory (D&Intel Lab), School of Computer Science and Engineering, Southeast University, China and the Robotics Control lab under the Interdisciplinary Research Centre for Aviation and Space Exploration (IRC-ASE), King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM), Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Dahri, F. H., Abro, G. E. M., Dahri, N. A., Laghari, A. A., & Ali, Z. A. (2024). Advancing Robotic Automation with Custom Sequential Deep CNN-Based Indoor Scene Recognition. IECE Transactions on Intelligent Systematics, 2(1), 14–26. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIS.2025.613103
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue