Abstract
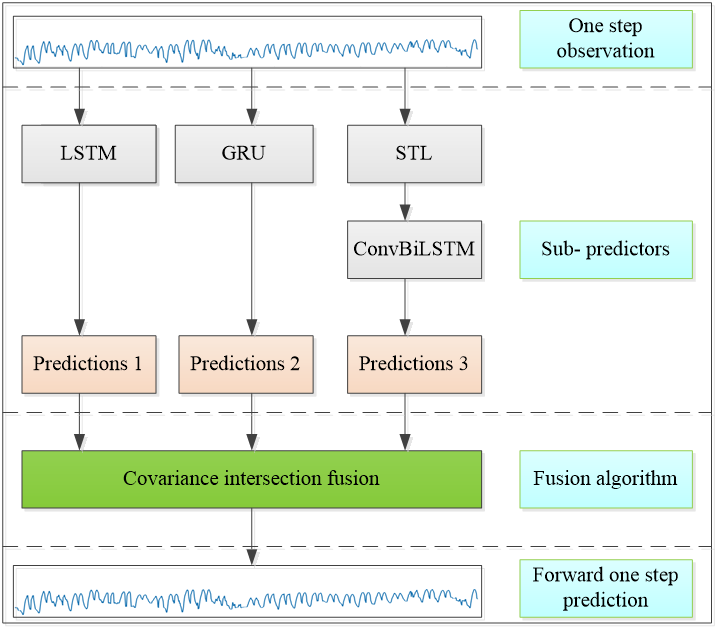
To predict future trends based on the data from sensors is an important technology for many applications, such as the Internet of Things, smart cities, etc. Based on the predicted results, further decisions and system controls can be made. Raw sensor data sets are often complex non-linear data with noise, which results in the difficulty of accurate prediction. This paper proposes a distributed deep prediction network based on a covariance intersection (CI) fusion algorithm in which the deep learning networks, such as long-term and short-term memory networks (LSTM) and gated recurrent unit networks (GRU) are fused by CI fusion algorithm to effectively develop the performance of prediction. Moreover, the variance is obtained to value the prediction results. The model is validated on the real weather dataset in Beijing. The experiments show that LSTM and GRU have their pros and cons for different data, CI fusion can develop the accuracy of the final predictions, and the entire framework has robust prediction results with a reasonable estimated variance.
Keywords
Deep Prediction Network
Covariance Intersection (CI) Fusion
Sensor Data Analytics
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China No. 62173002.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Ren, H., Wang, Y., & Ma, H. (2024). Deep Prediction Network Based on Covariance Intersection Fusion for Sensor Data. IECE Transactions on Intelligent Systematics, 1(1), 10–18. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIS.2024.136898
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue