Abstract
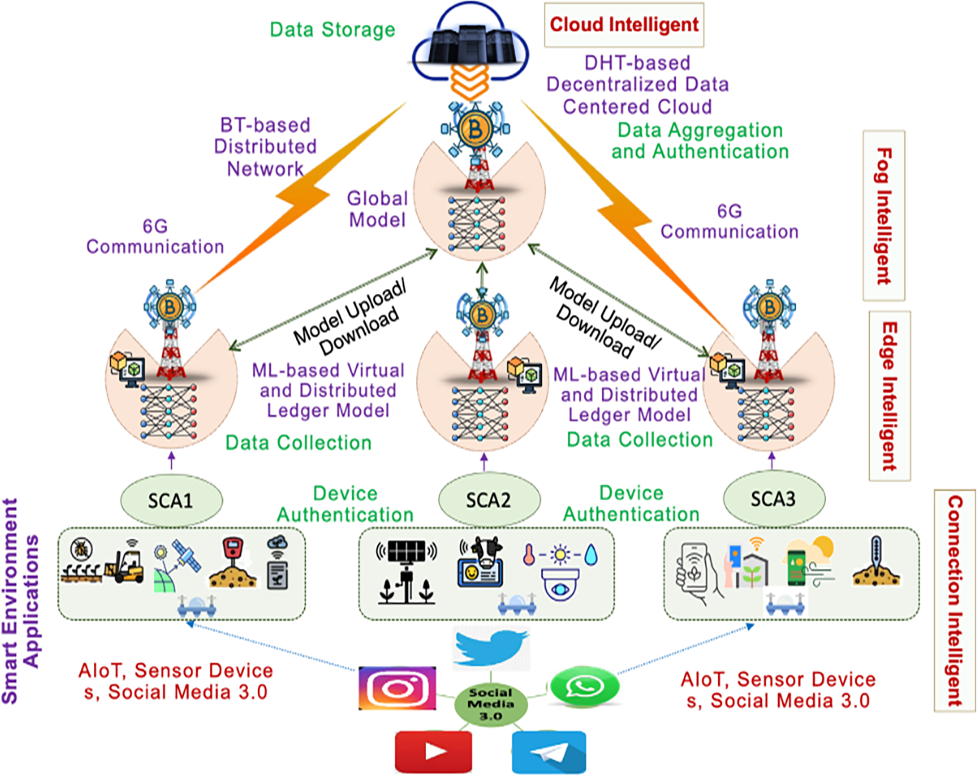
Smart Environment is rapidly growing with the inclusion of Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) when it connects to future communication and social media networks. Security and privacy are significant challenges, including data integrity, account hijacking, cybersecurity, and cyberbullying. To mitigate these challenges, Social Media 3.0 is utilized with advanced emerging technologies such as Blockchain, Federated Learning (FL), and others and offers solutions in existing research. This article comprehensively reviews and proposes Next-Generation Technologies for Secure Future Communication Service Scenario for Smart Environment and Social-Media 3.0. We discuss existing attacks with their classification that can threaten the personal information of a Future Communication-based Smart Environment, then offer countermeasure solutions. FL with AIoT is discussed to preserve the privacy and security of smart environment applications with live projects under the implementation of the Dubai Blockchain Strategy, ADEPT, and many more. Blockchain is utilized at the proposed service scenario's edge, fog, and cloud intelligent layers for secure future communication; FL trains local models that aggregate to form global models trained over diverse Smart Environments. Finally, several challenges and open issues of integrating emerging technologies for Smart Environment and Social-Media 3.0 applications and future directions are discussed in the last section.
Keywords
smart environment (SE)
blockchain, federated Learning (FL)
social media, internet of things (IoT)
Funding
This research was supported by the Research Seed Grant funded by the Marwadi University, Rajkot, Gujarat (MU/R\&D/22- 23/MRP/FT13).
Cite This Article
APA Style
Kurde, A., & Singh, S. K. (2024). Next-Generation Technologies for Secure Future Communication-based Social-Media 3.0 and Smart Environment. IECE Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control, 1(2), 101–125. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSCC.2024.322898
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue