Abstract
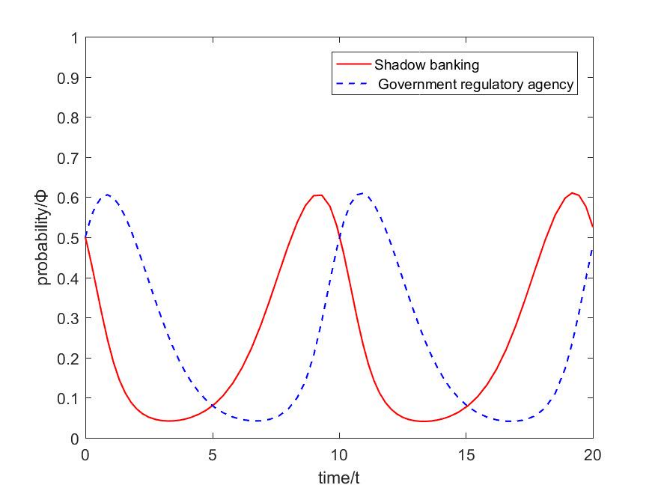
Both the shadow banking and the government regulatory agencies are bounded rational subjects, and they will constantly adjust the game according to the change of the other party's strategy when making decisions. Therefore, it has become an effective way to explore the government regulatory issues of China's shadow banking with the application of evolutionary game theory. By constructing the evolutionary game model of shadow banking and government regulatory authorities, this paper analyzes the dynamic adjustment relationship between the strategy choice of shadow banking and government regulatory authorities, and concludes that the operating income and cost of shadow banking, the intensity of rewards and punishments and the supervision cost of government regulatory authorities are the important factors affecting the decision-making of the two. It is necessary to improve the information disclosure system of shadow banking, strengthen the reward and punishment mechanism for shadow banking, innovate the ways and methods of government supervision of shadow banking, smooth and improve the channels and mechanisms for coordinating government supervision, and guide the compliance operation of shadow banking.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Li, R., Yang, J., & Yan, Y. (2024). Evolutionary Game Simulation Analysis of Government Supervision of Shadow Banking in China. IECE Transactions on Social Statistics and Computing, 1(2), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSSC.2024.775392
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue