Abstract
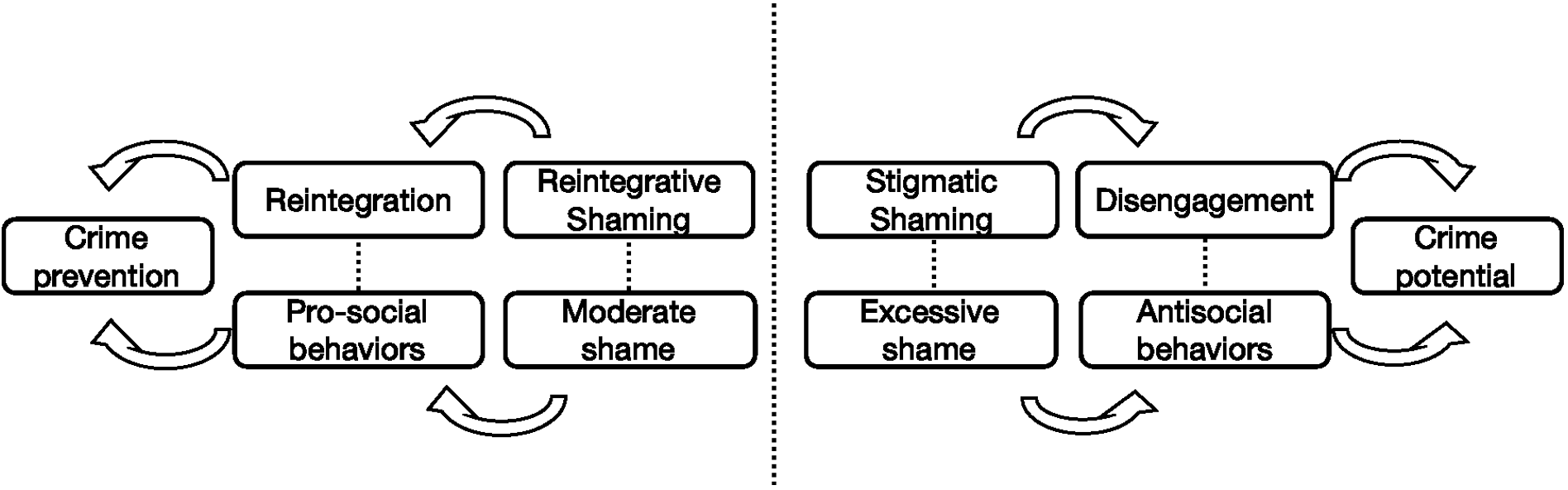
Taking China as an example, “Reintegrative Shaming” can provide new ideas for the progress of juvenile criminal justice, especially educational correction. Although “Reintegrative Shaming” is often regarded as a philosophy of law, it is not only a theory but also a feasible method under the verification of psychology. Because the emotional experience of shame has a moderating effect on the behavioral habits of minors, appropriate forgiveness can avoid the negative effects of excessive shame. In order to effectively apply “Reintegrative Shaming” in juvenile criminal justice, it is also necessary to rationalize the conduct of persuasive sessions and to give due consideration to the participants.
Keywords
reintegrative shaming
juvenile criminal justice
crime prevention
Funding
This work was supported by the Youth Innovation Talent Project of Ordinary Universities of Guangdong Province under Grant 2023WQNCX110.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Shi, M. (2024). The Role of “Reintegrative Shaming” in Juvenile Criminal Justice. IECE Transactions on Social Statistics and Computing, 1(3), 83–88. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSSC.2024.909972
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue