Chinese Journal of Information Fusion | Volume 1, Issue 3: 226-242, 2024 | DOI: 10.62762/CJIF.2024.655617
Abstract
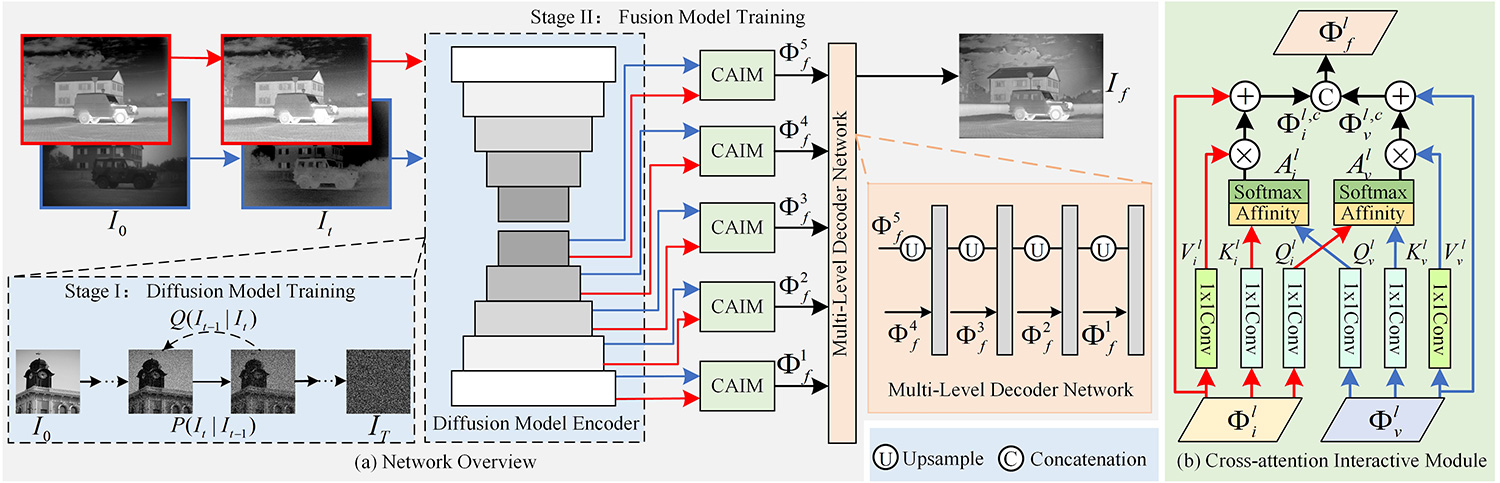
Image fusion aims to integrate complementary information from different sensors into a single fused output for superior visual description and scene understanding. The existing GAN-based fusion methods generally suffer from multiple challenges, such as unexplainable mechanism, unstable training, and mode collapse, which may affect the fusion quality. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces a diffusion model guided cross-attention learning network, termed as DMFuse, for infrared and visible image fusion. Firstly, to improve the diffusion inference efficiency, we compress the quadruple channels of the denoising UNet network to achieve more efficient and robust model for fusion tas... More >
Graphical Abstract