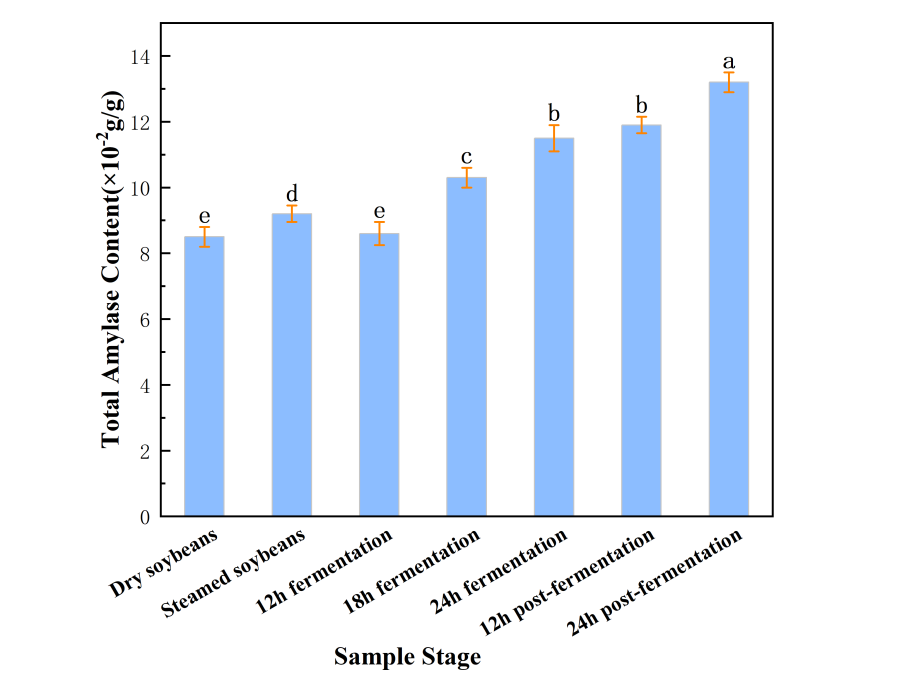
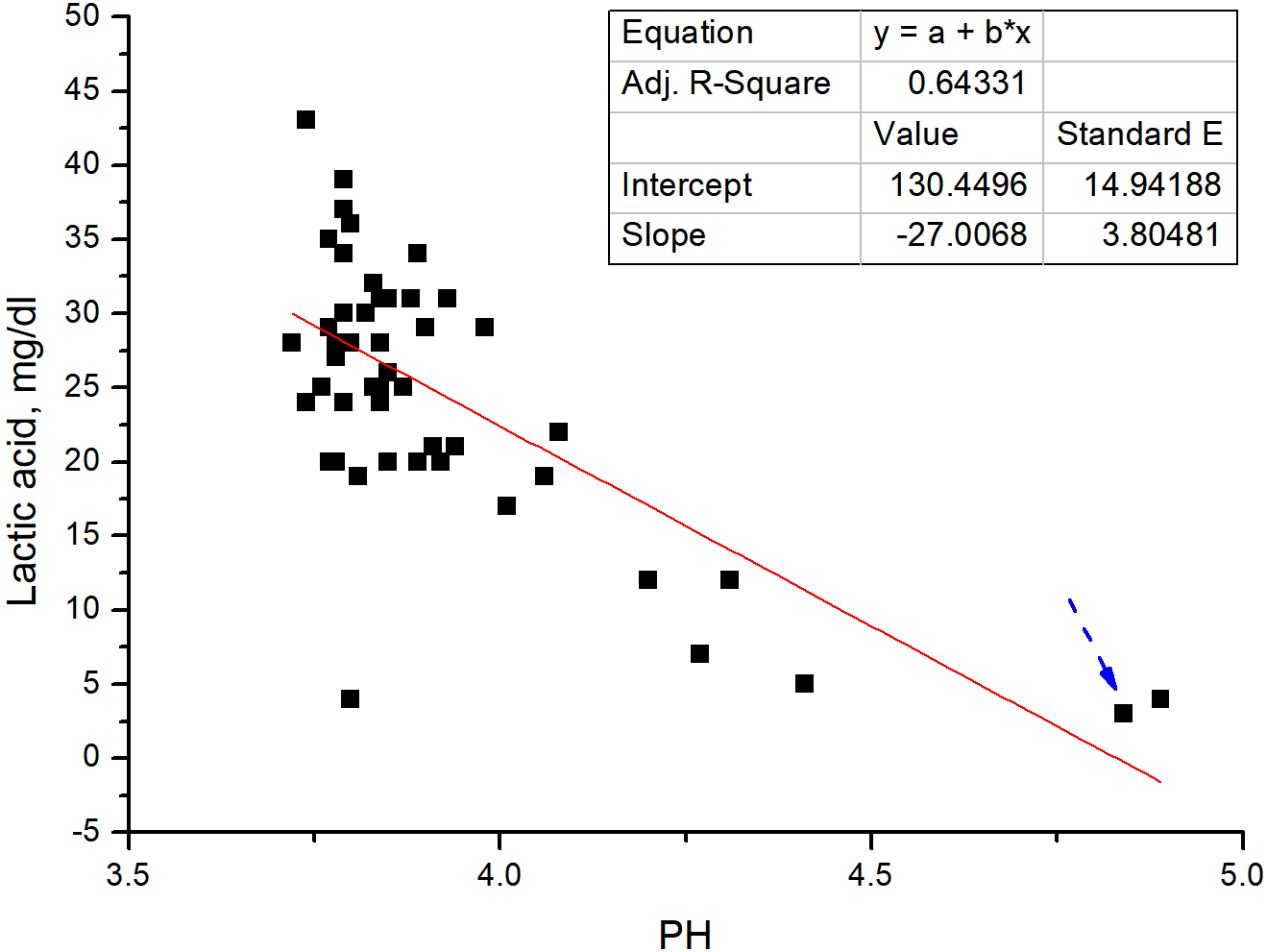
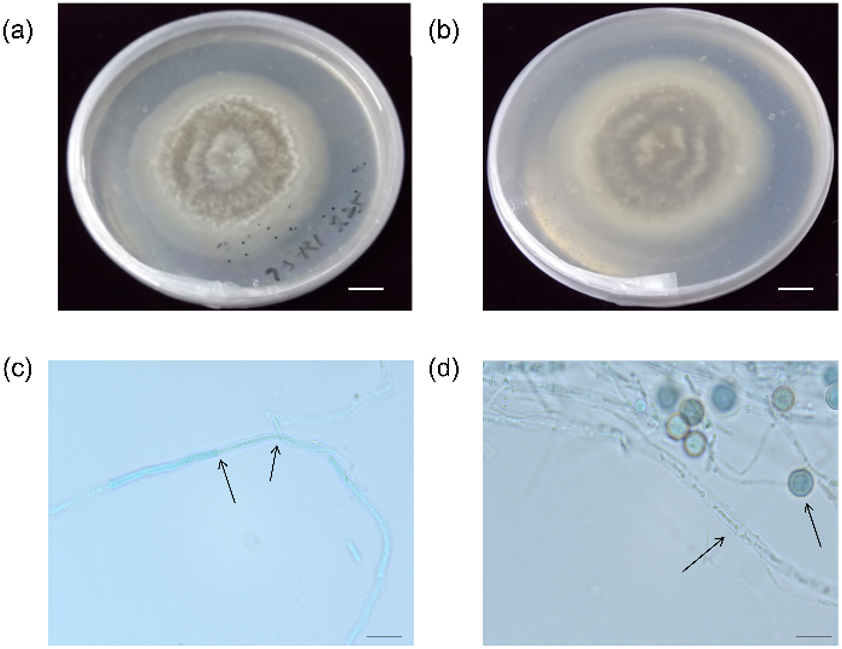
Agricultural Science and Food Processing | Volume 2, Issue 1: 56-67, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/ASFP.2025.993704
Abstract
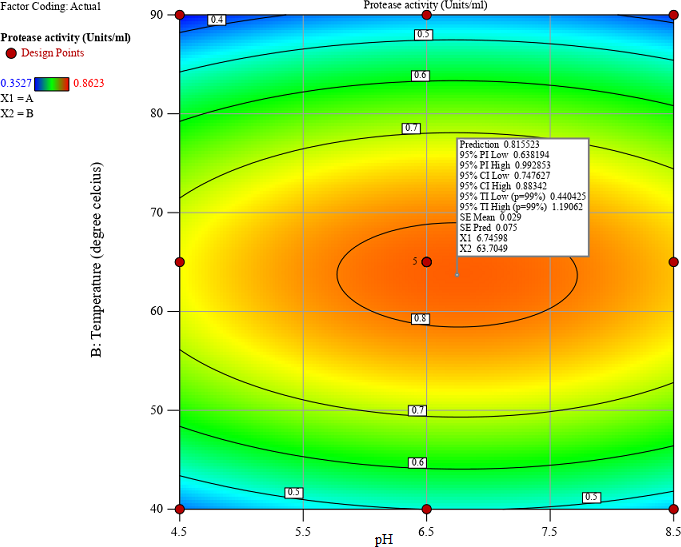
This study investigates the impact of three precipitation methods, ammonium sulfate (40%), acetone, and acetone with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) on the yield and activity
of protease extracted from Averrhoa carambola (starfruit) at various maturity stages (unripe, semi-ripe, and ripe). The study employed response surface methodology (RSM) to optimize hydrolysis conditions, specifically temperature, and pH, for maximum proteolytic activity. The proteases were incubated in buffers at pH values ranging from 3.5 to 8.5 for 12 hours, and the proteolytic activity was assessed. Additionally, temperature effects were evaluated by incubating proteases at temperatures between 40◦C and 90◦C. The st... More >
Graphical Abstract