IECE Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control | Volume 1, Issue 2: 136-153, 2024 | DOI: 10.62762/TSCC.2024.626147
Abstract
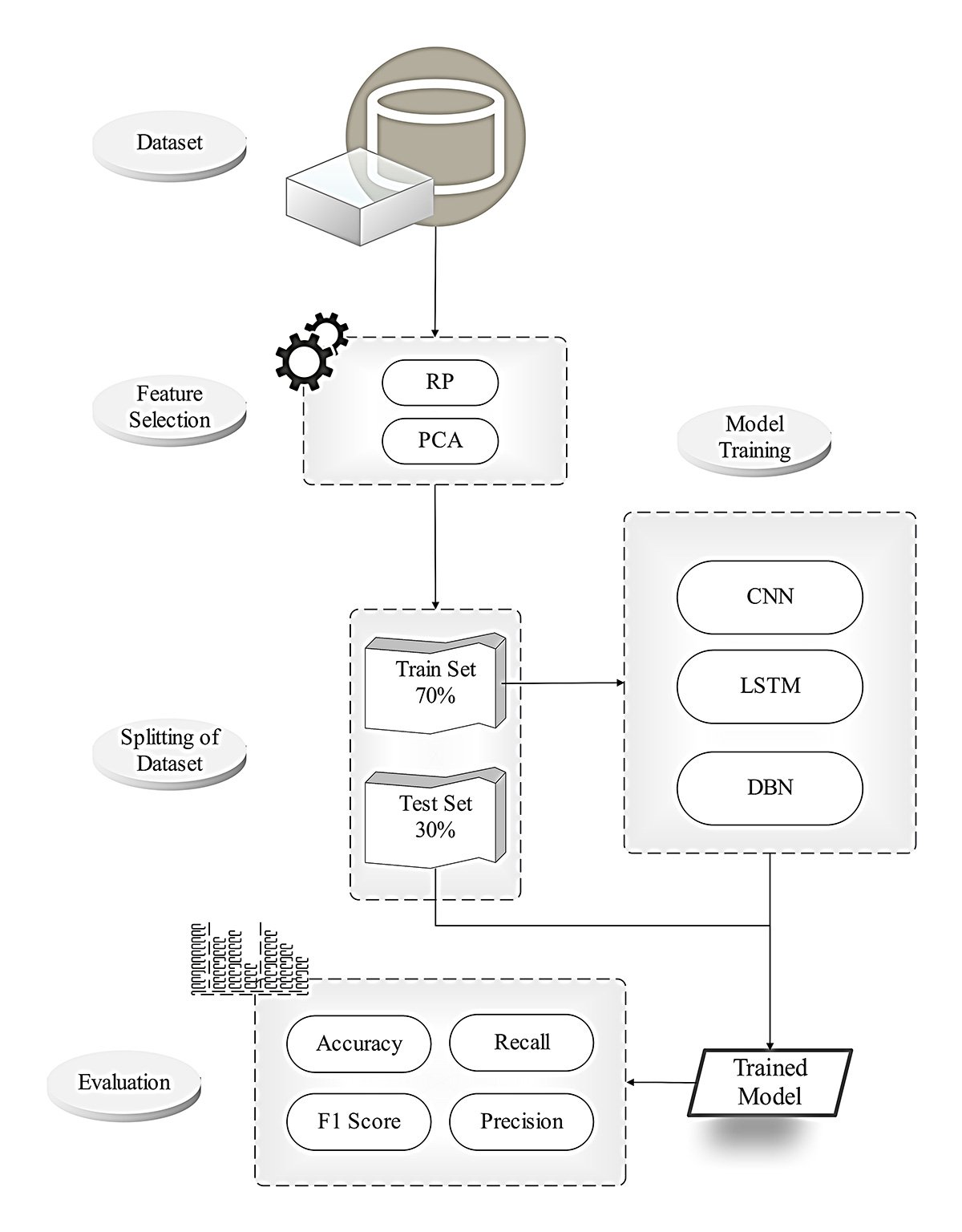
In recent years, vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs) have faced growing security concerns, particularly from Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. These attacks flood the network with malicious traffic, disrupting services and compromising resource availability. While various techniques have been proposed to address these threats, this study presents an optimized framework leveraging advanced deep-learning models for improved detection accuracy. The proposed Intrusion Detection System (IDS) employs Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and Deep Belief Networks (DBN) alongside robust feature selection techniques, Random Projecti... More >
Graphical Abstract