IECE Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control | Volume 1, Issue 2: 126-135, 2024 | DOI: 10.62762/TSCC.2024.672831
Abstract
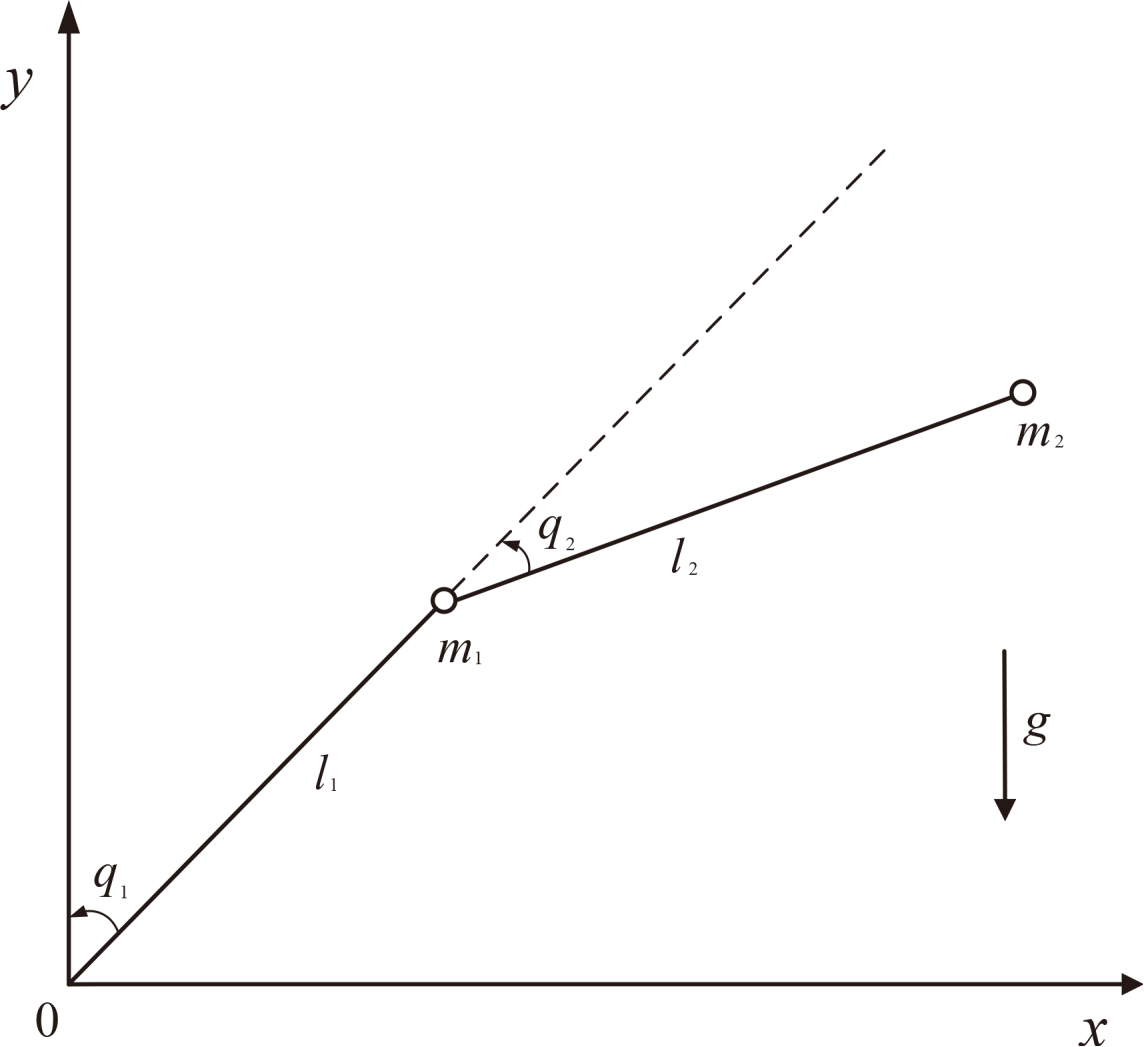
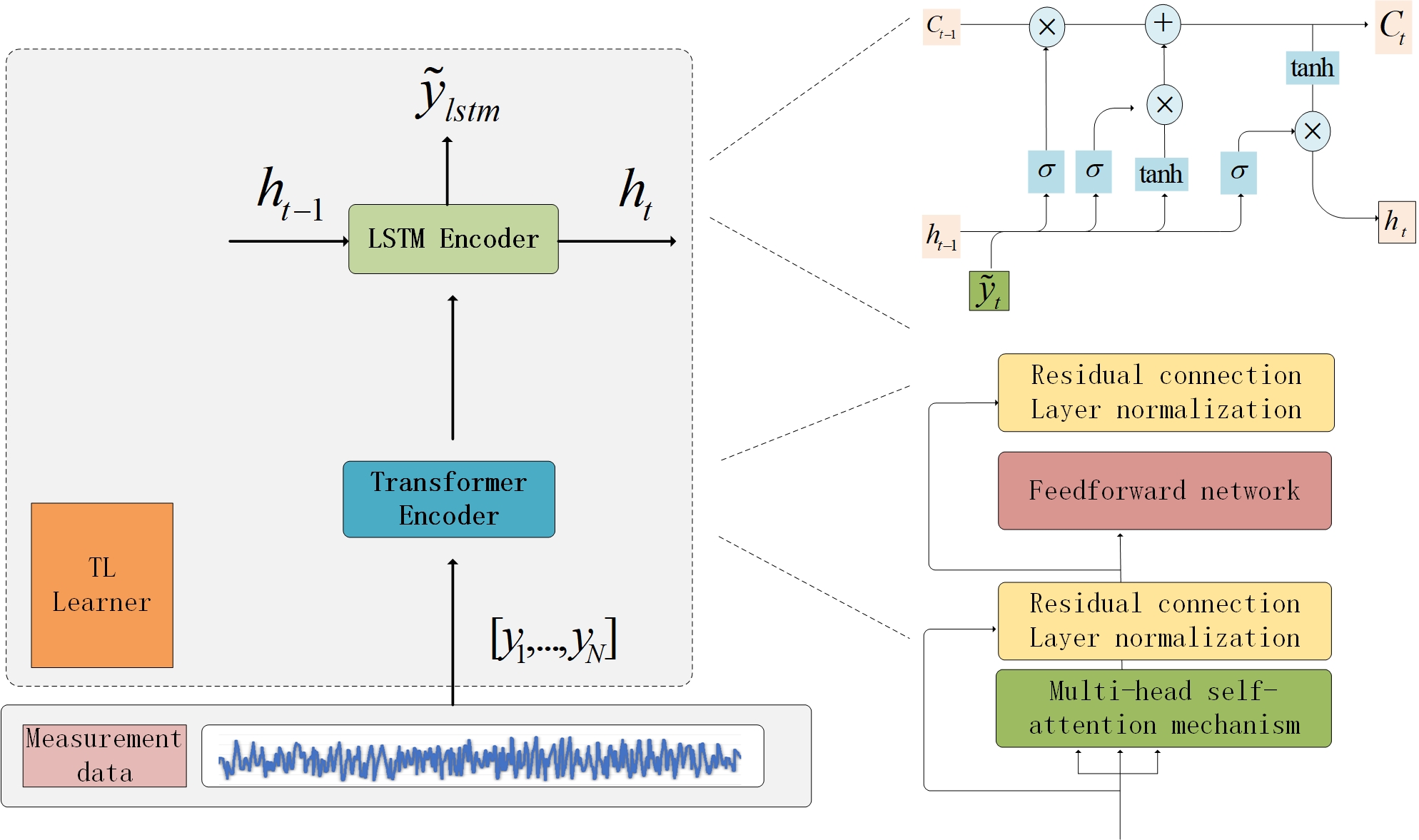
In engineering applications, high-precision tracking control is crucial for robotic manipulators to successfully complete complex operational tasks. To achieve this goal, this study proposes an adaptive tunable predefined-time backstepping control strategy for uncertain robotic manipulators with external disturbances and model uncertainties. By establishing a novel practical predefined-time stability criterion, a tunable predefined-time backstepping controller is systematically presented, allowing the upper bound of tracking error settling time to be precisely determined by adjusting only one control parameter. To accurately address lumped uncertainty, two updating laws are designed: a fuzz... More >
Graphical Abstract