IECE Transactions on Intelligent Systematics | Volume 2, Issue 1: 38-48, 2025 | DOI:10.62762/TIS.2024.564569
Abstract
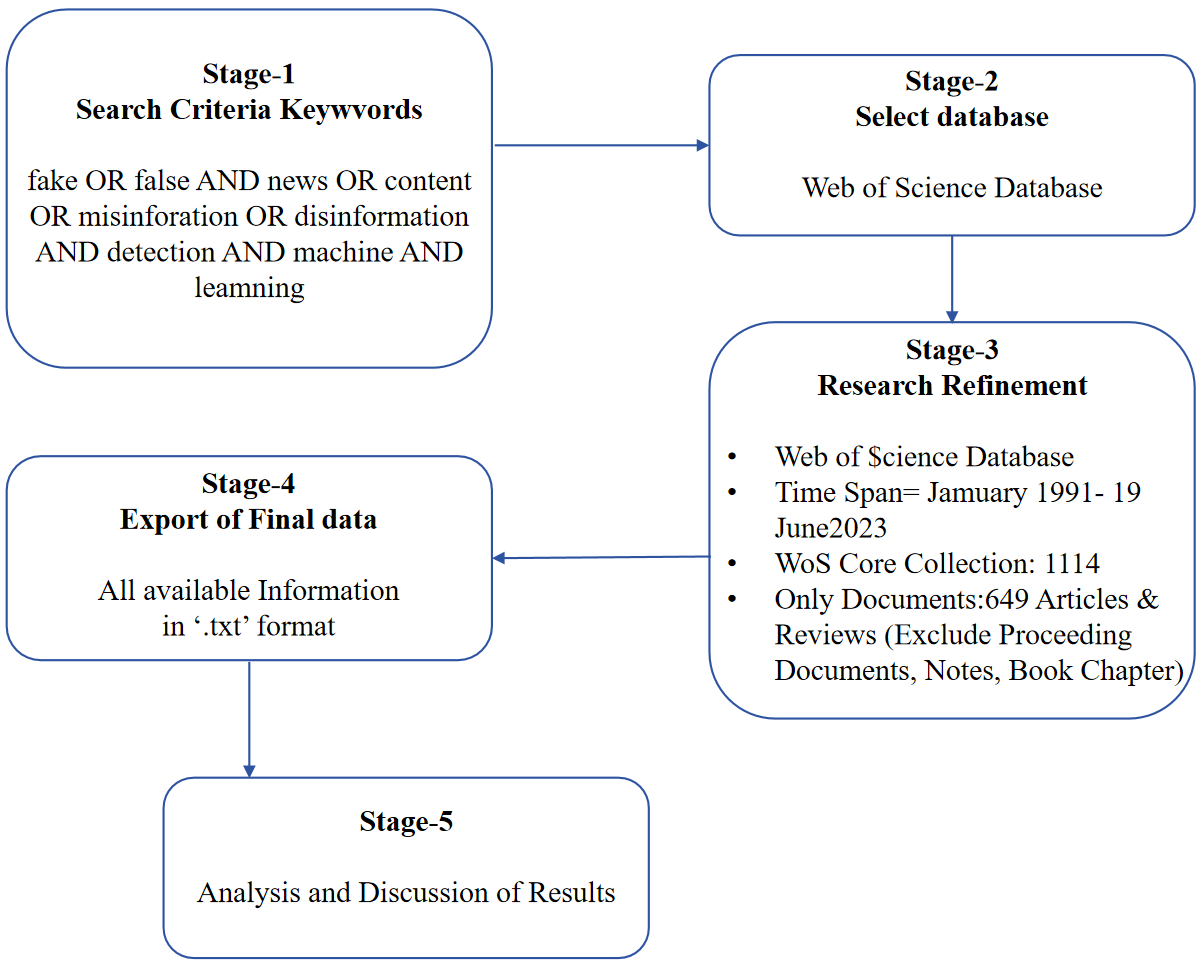
In the modern world, disseminating false information is a problem that must be addressed, and algorithms based on machine learning are used to spot and stop the spread of incorrect information. Due to the current unregulated development of false news fabrication and dissemination, democracy is continuously under threat. Fake news may mislead individuals while influencing them because of its persuasiveness and life sciences. Using data from the Web of Science, this study undertakes a bibliometric analysis of research on the application of machine learning for fake news identification. The research underscores the need for a streamlined approach to analyze data exclusively from the Web of Scie... More >
Graphical Abstract