IECE Transactions on Intelligent Systematics | Volume 1, Issue 3: 190-202, 2024 | DOI: 10.62762/TIS.2024.751418
Abstract
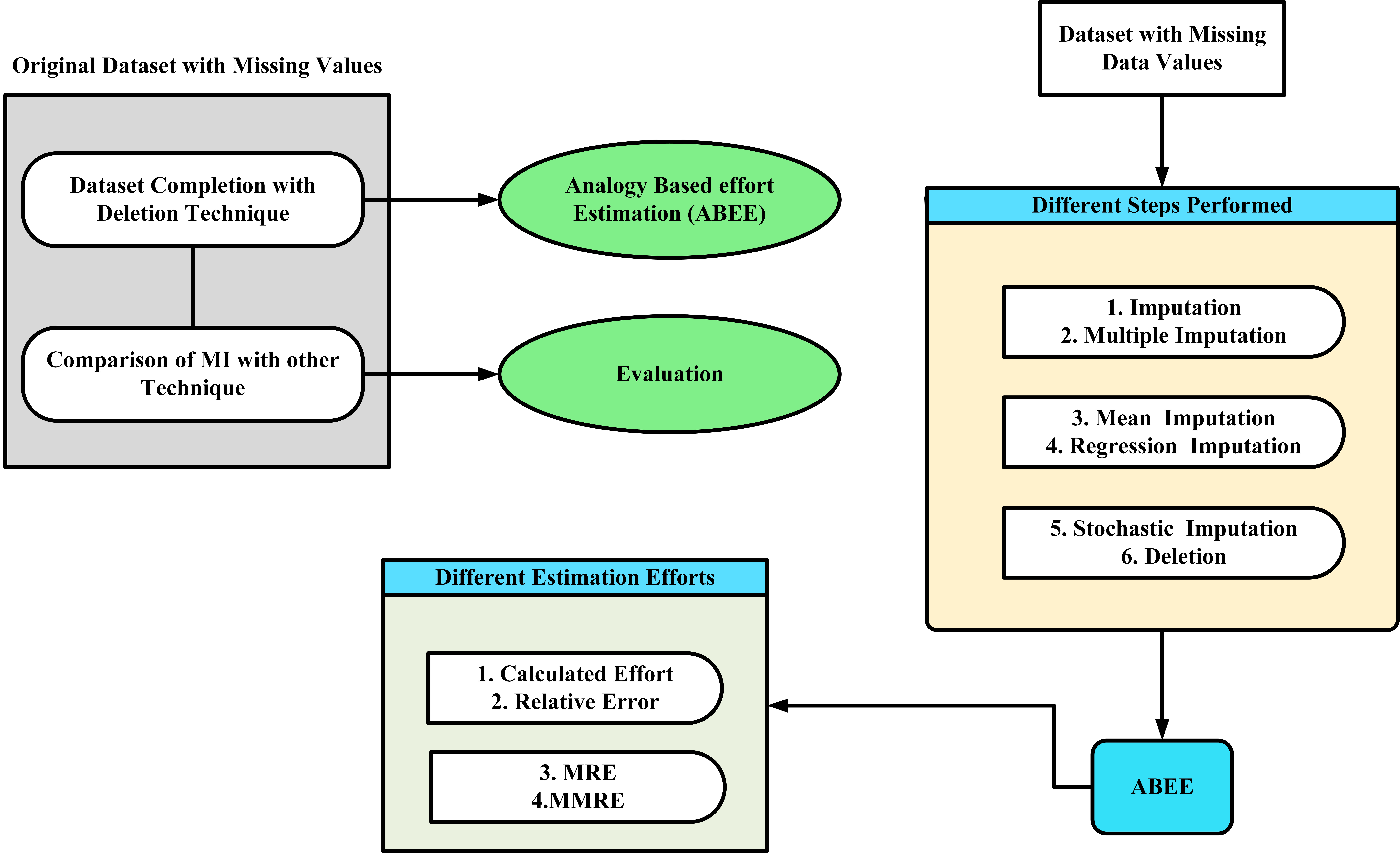
The challenge of accurately estimating effort for software development projects is critical for project managers (PM) and researchers. A common issue they encounter is missing data values in datasets, which complicates effort estimation (EE). While several models have been introduced to address this issue, none have proven entirely effective. The Analogy-Based Effort Estimation (ABEE) model is the most widely used approach, relying on historical data for estimation. However, the common practice of deleting cases or cells with missing observations results in a reduction of statistical power and negatively impacts the performance of ABEE, leading to inefficiencies and biases. This study employ... More >
Graphical Abstract