Agricultural Science and Food Processing | Volume 1, Issue 1: 38-47, 2024 | DOI: 10.62762/ASFP.2024.541137
Abstract
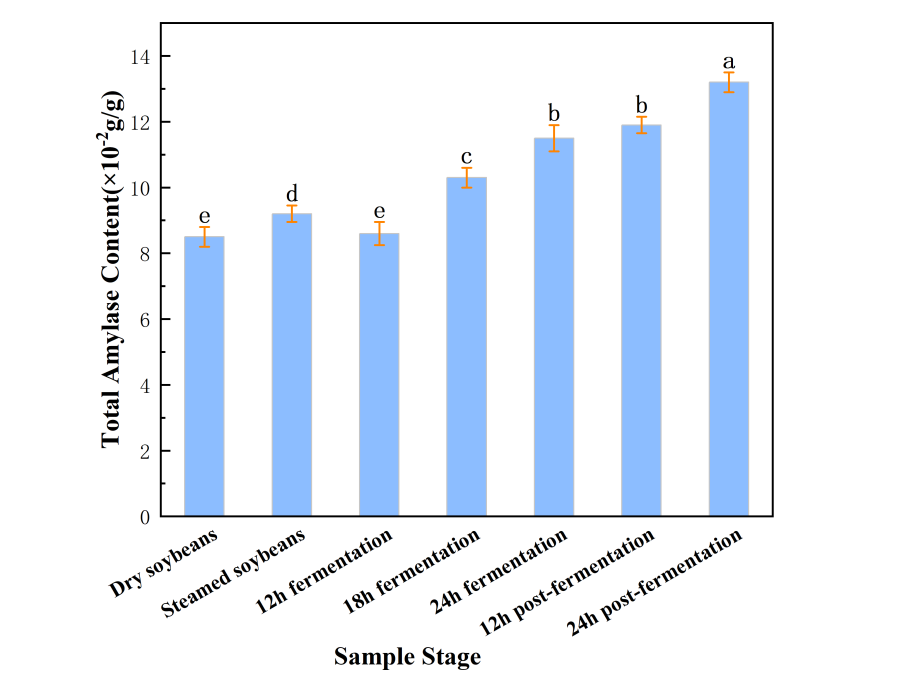
To investigate the changes of bioactive compounds during natto fermentation, this study focused on the variations in the levels of phenolic compounds, isoflavones, and antioxidant capabilities at various stages of the natto fermentation. Additionally, the impact of simulated in vitro digestion process of natto on phenolic compounds, isoflavones, and antioxidant capabilities was evaluated. The results indicated that fermentation process increased the phenolic content of 60.56%, while the isoflavone content decreased in 63.30%. Following in vitro digestion, the total phenolics content exhibited a release rate of 70.64%, while the isoflavones content had a residual rate of 21.79%. Antioxidant a... More >
Graphical Abstract