Sustainable Intelligent Infrastructure | Volume 1, Issue 1: 19-28, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/SII.2025.498283
Abstract
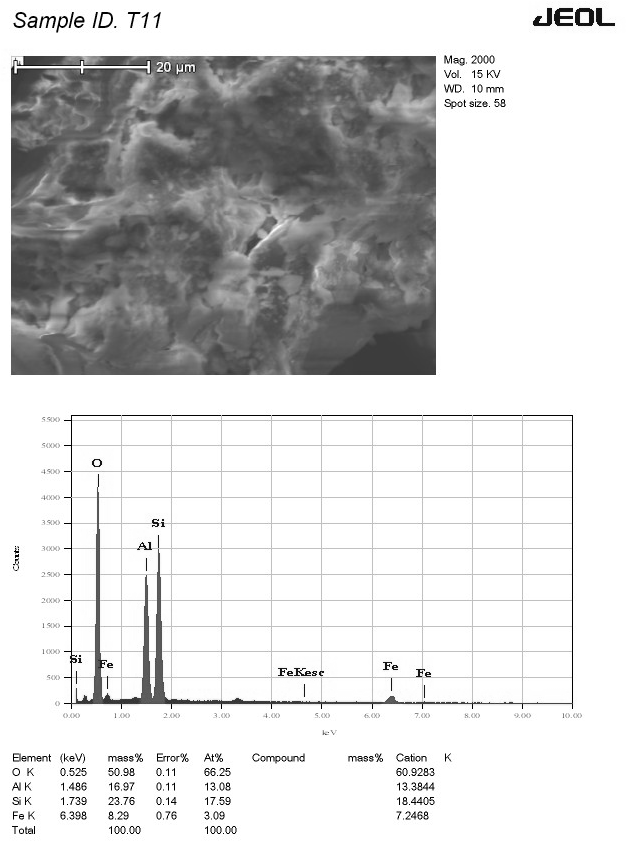
This study evaluated the potential of readily available Indian soils, red soil (Bengaluru) and black cotton soil (Belgaum), as sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to synthetic landfill liners for heavy metal containment. Utilizing Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), we characterized the soil's microstructural properties and elemental composition to assess their adsorption capabilities. To enhance metal capture, soils were amended with lime, cement, and fly ash. Batch leaching experiments, simulating landfill conditions with copper and chromium contamination, quantified adsorption efficiency. Microscopic analysis of leached samples using SEM an... More >
Graphical Abstract