Abstract
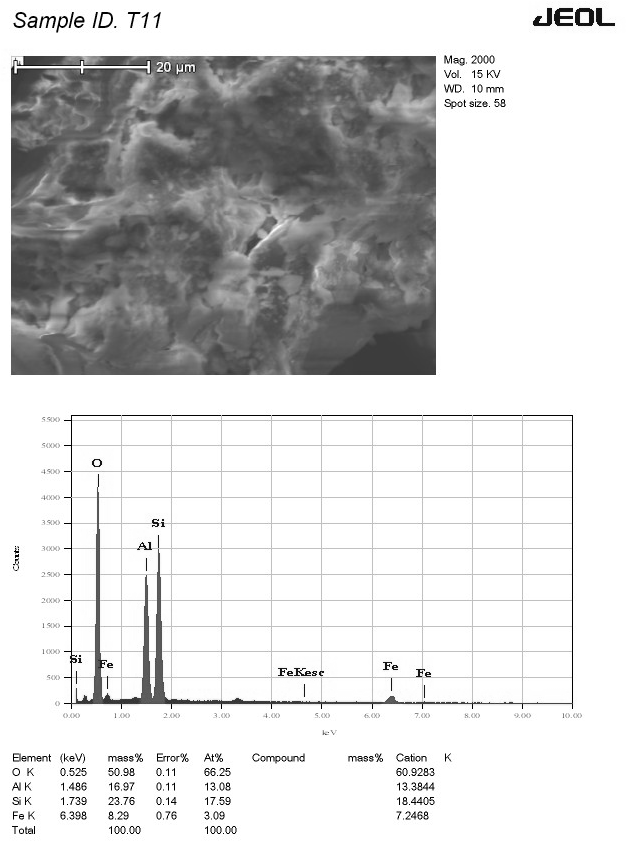
This study evaluated the potential of readily available Indian soils, red soil (Bengaluru) and black cotton soil (Belgaum), as sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to synthetic landfill liners for heavy metal containment. Utilizing Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), we characterized the soil's microstructural properties and elemental composition to assess their adsorption capabilities. To enhance metal capture, soils were amended with lime, cement, and fly ash. Batch leaching experiments, simulating landfill conditions with copper and chromium contamination, quantified adsorption efficiency. Microscopic analysis of leached samples using SEM and EDS corroborated macroscopic findings, revealing key adsorption mechanisms such as particle aggregation and the formation of binding compounds. Black cotton soil, particularly when amended, exhibited superior adsorption, likely due to its higher organic matter content. This integrated approach, linking microscopic observations to macroscopic performance, demonstrates the viability of these local soils, especially with additives, for effective and sustainable landfill liner applications.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Mohammed, S. A. S., & Moghal, A. A. B. (2025). Investigating the Adsorption Properties of Soil Additive Mixtures Using Microstructural Characterization Techniques for Liner Applications. Sustainable Intelligent Infrastructure, 1(1), 19–28. https://doi.org/10.62762/SII.2025.498283
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 