Chinese Journal of Information Fusion | Volume 1, Issue 2: 160-174, 2024 | DOI: 10.62762/CJIF.2024.734267
Abstract
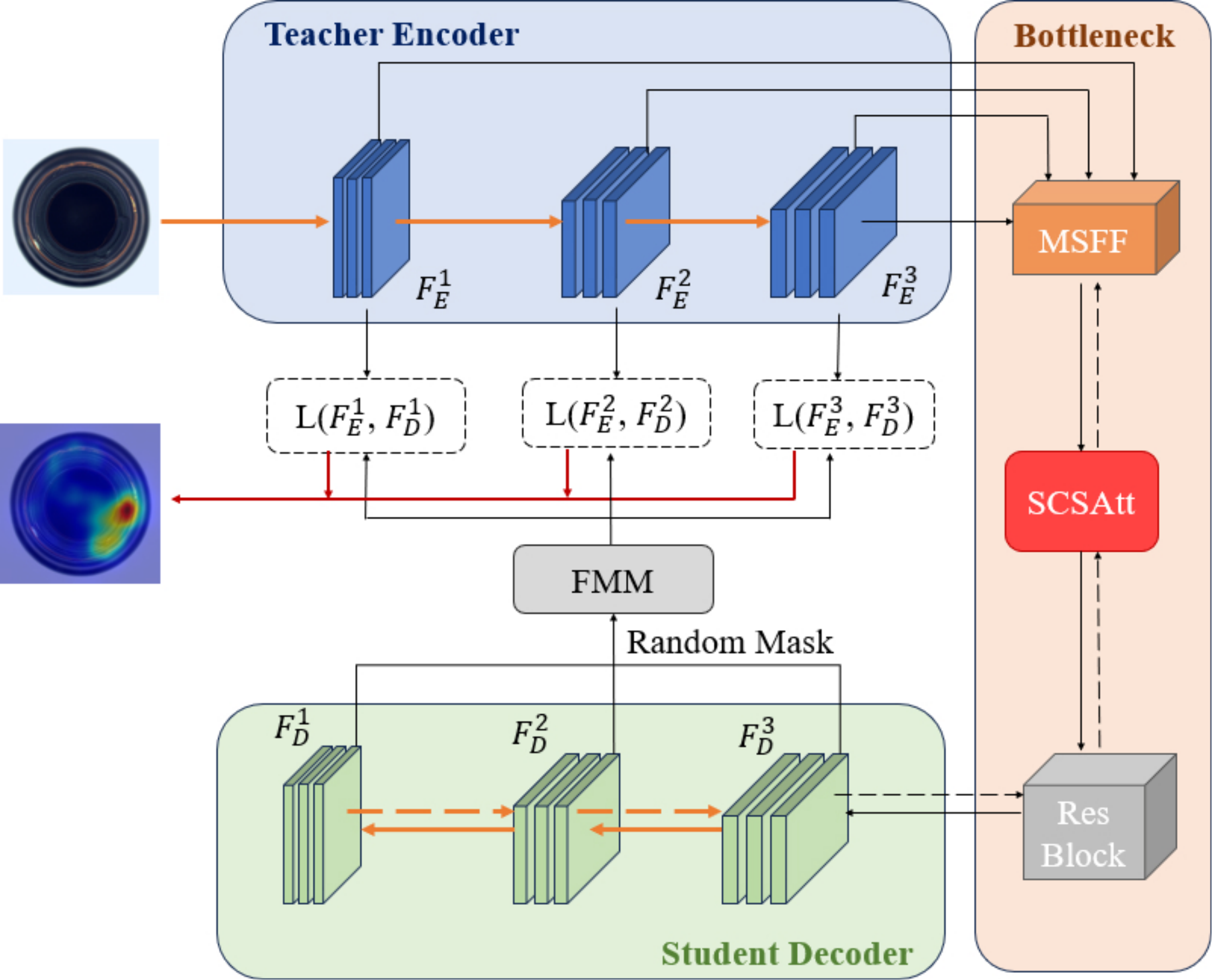
In the realm of industrial defect detection, unsupervised anomaly detection methods draw considerable attention as a result of their exceptional accomplishments. Among these, knowledge distillation-based methods have emerged as a prominent research focus, favored for their streamlined architecture, precision, and efficiency. However, the challenge of characterizing the variability in anomaly samples hinders the accuracy of detection. To address this issue, our research presents a novel approach for anomaly detection and localization, leveraging the concept of inverse knowledge distillation as its cornerstone. We employ the encoder as the guiding teacher model and designate the decoder as the... More >
Graphical Abstract