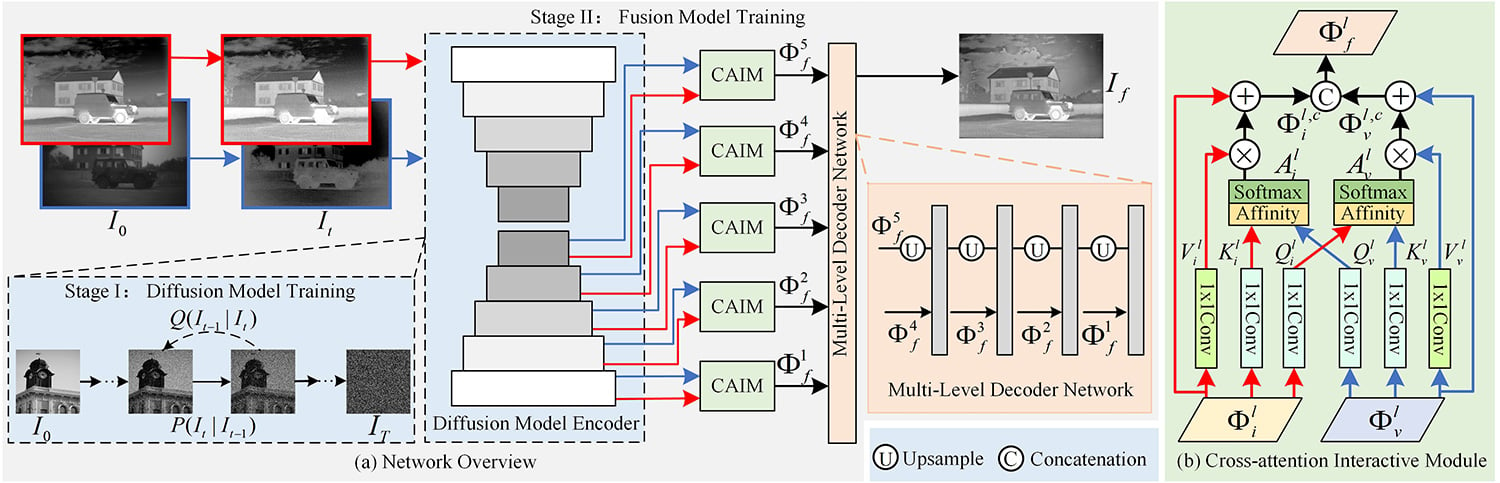
Chinese Journal of Information Fusion | Volume 2, Issue 2: 100-111, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/CJIF.2025.986522
Abstract
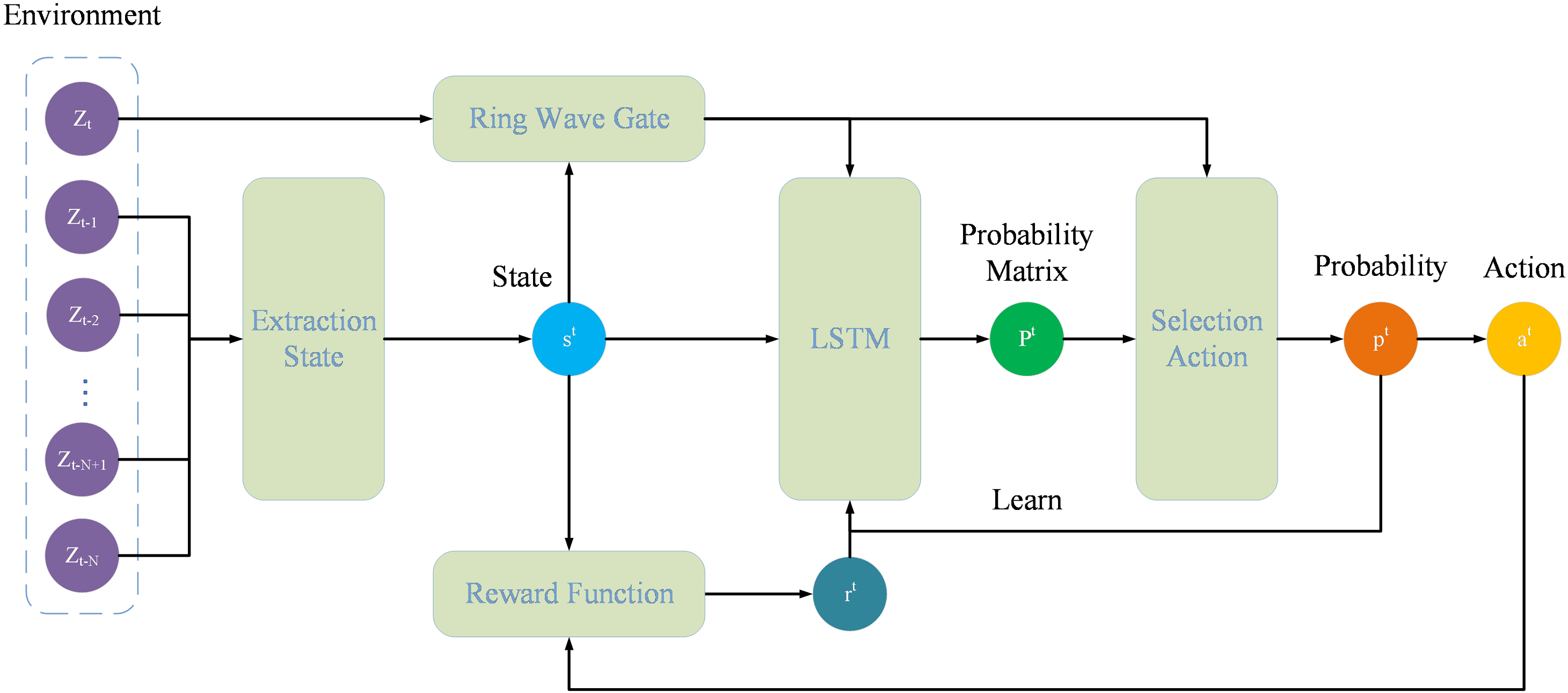
To address the performance degradation of traditional data association algorithms caused by unknown target motion models, environmental interference, and strong maneuvering behaviors in complex dynamic scenarios, this paper proposes an innovative fusion algorithm that integrates reinforcement learning and deep learning. By constructing a policy network that combines Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) memory units and reinforcement learning dynamic decision-making, a dynamic prediction model for "measurement-target" association probability is established. Additionally, a hybrid predictor incorporating Bayesian networks and multi-order curve fitting is designed to formulate the reward function. To... More >
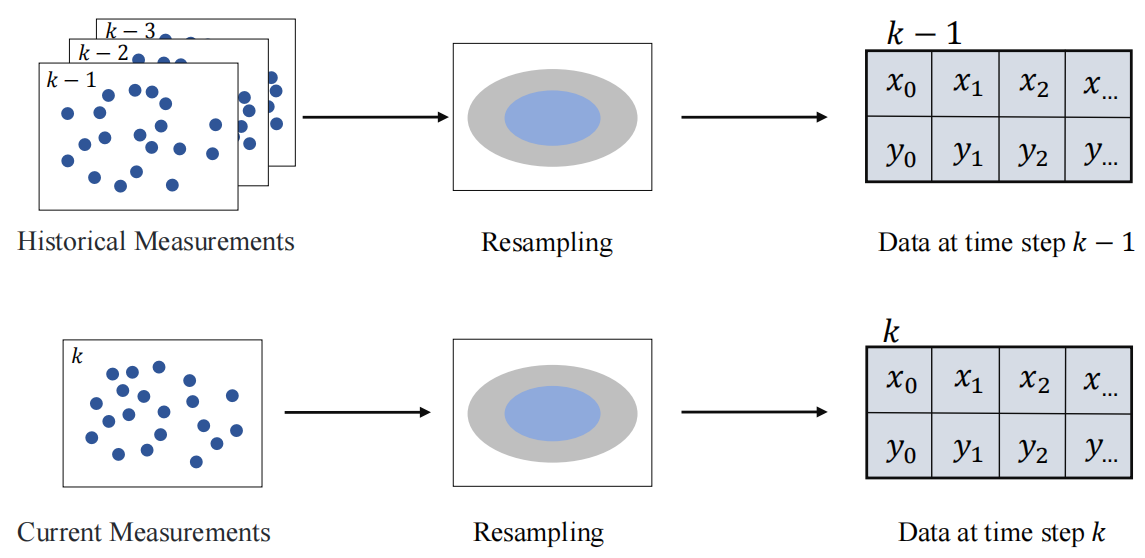
Graphical Abstract