Abstract
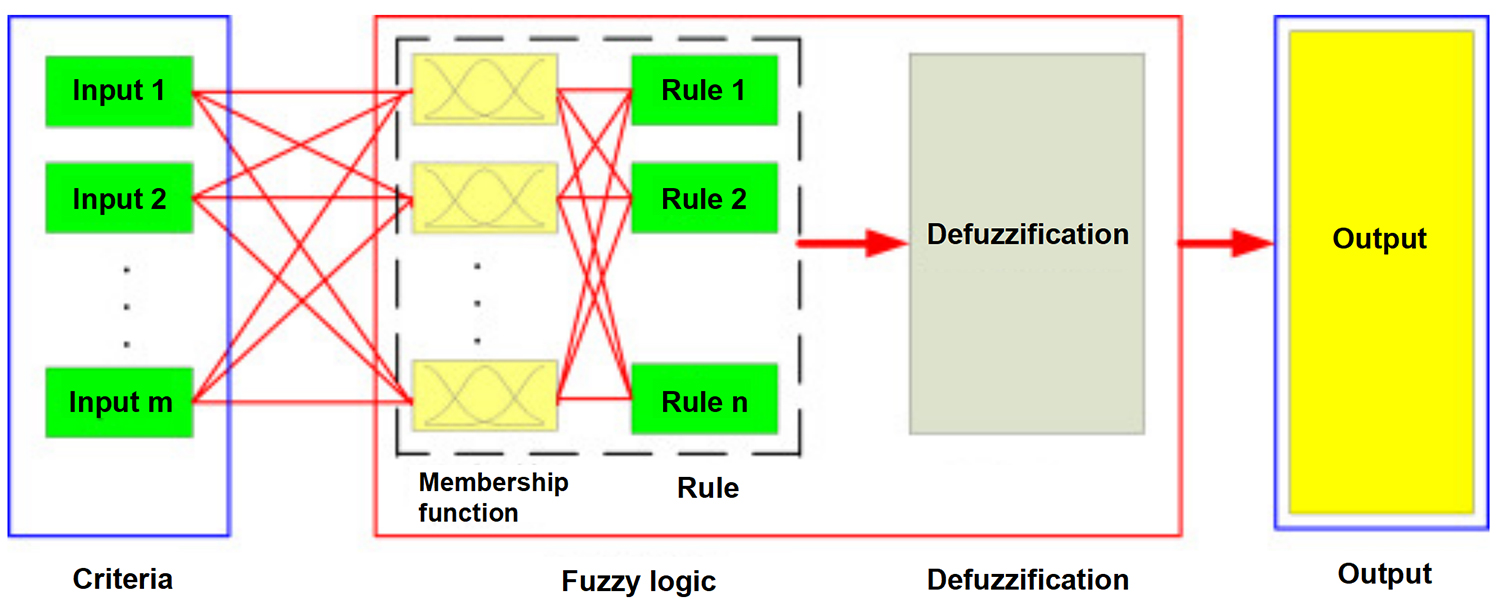
Pavement maintenance is a critical aspect of transportation and infrastructure management, as it directly impacts traffic flow, vehicle maintenance, safety and accident rate. Effective prediction and prevention of pavement deterioration are essential for optimizing pavement maintenance strategies, reducing cost, and ensuring the lifespan or longevity of transportation. This study presents the development of Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) for predicting pavement deterioration. The data used for this analysis is a historical data and field investigation data from the Cross River State pavement Maintenance Agency, Calabar, Nigeria. The ANFIS model was trained using a dataset with input variables, the outcome from the membership functions shows that in1=4.4, in2=3.15, in3=13.5 and output variable (out1=0.541). The model consists of 270 nodes, 33 fuzzy set, and utilizes sub clustering (FIS type), hybrid optimization method, Gaussmf membership function, and wtaver defuzzification. The study result showed that the ANFIS model accurately predicted pavement deterioration with Root mean Squared Error (RMSE) 0f 0.851716. The developed ANFIS model can be used by transportation agencies to predict pavement deterioration and prioritize maintenance activities. The Model’s ability to handle nonlinear relationships and uncertainty makes it a valuable tool for pavement management.
Keywords
pavement deterioration
adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS)
pavement maintenance
pavement management
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Ujong, J. A., Onyelowe, F. K. C., Emmanuel, E., Vishnupriyan, M., Ibe, K. C., Ugorji, B., Nwa-David, C., Ihenna, L., & Obimba-Wogu, J. (2025). Development of an Adaptive Neuro-fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) for Predicting Pavement Deterioration. Sustainable Intelligent Infrastructure, 1(1), 39–51. https://doi.org/10.62762/SII.2025.494563
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 