Abstract
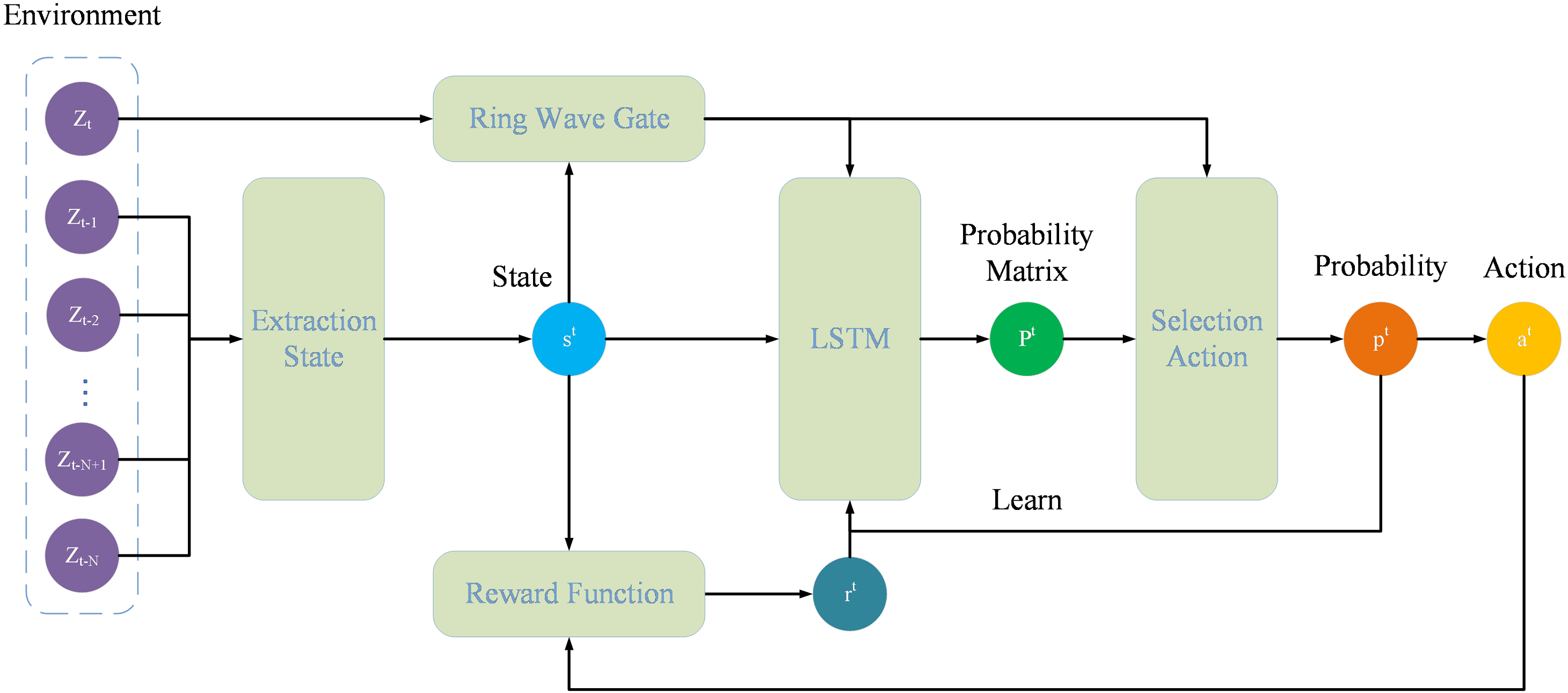
To address the performance degradation of traditional data association algorithms caused by unknown target motion models, environmental interference, and strong maneuvering behaviors in complex dynamic scenarios, this paper proposes an innovative fusion algorithm that integrates reinforcement learning and deep learning. By constructing a policy network that combines Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) memory units and reinforcement learning dynamic decision-making, a dynamic prediction model for "measurement-target" association probability is established. Additionally, a hybrid predictor incorporating Bayesian networks and multi-order curve fitting is designed to formulate the reward function. To tackle practical interference, a dynamic ring gate screening mechanism and a trajectory consistency-based error correction module are developed, effectively suppressing clutter interference and enabling autonomous correction of association errors. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves association accuracy in high-noise environments compared to traditional algorithms, enhancing robustness in complex unknown scenarios.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Gu, X., Ding, Z., Xia, S., & Xiong, W. (2025). Dynamic Target Association Algorithm for Unknown Models and Strong Interference. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion, 2(2), 100–111. https://doi.org/10.62762/CJIF.2025.986522
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 