Abstract
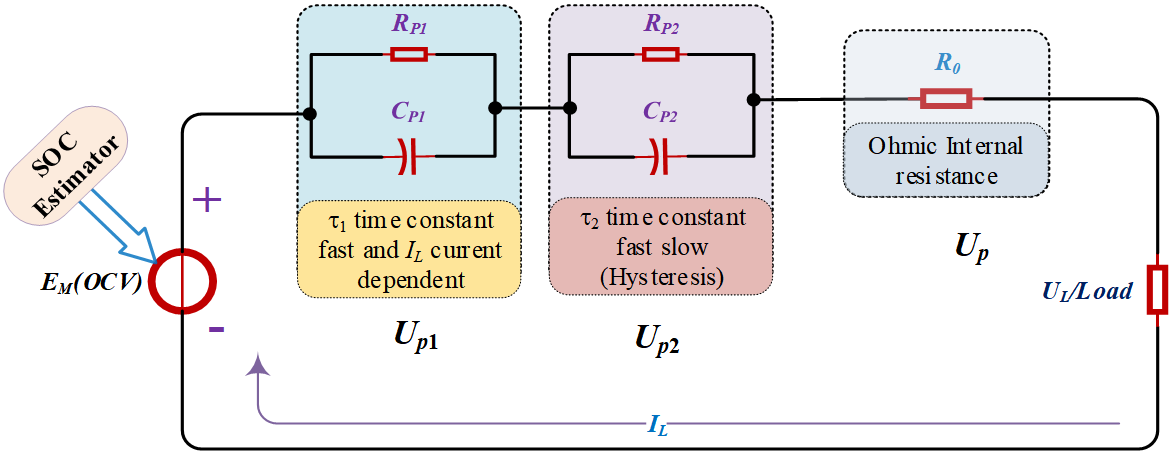
Accurately determining the state of charge (SOC) is a critical factor in effective energy management for electric vehicles (EVs). Therefore, SOC variations in battery packs must be assessed with high precision. To simulate the complex processes within EVs that involve lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), an appropriate battery model is essential. Accurate parameter extraction through algorithmic methods is key to reliable SOC estimation. A dynamic, high-order equivalent circuit model, featuring two RC pairs in series with the battery's internal resistance, is employed to enhance parameter extraction. The values of the RC pairs are derived by solving equations that characterize the operational states of the high-order circuit. Parameter identification is facilitated by the hybrid pulse power characterization test, which enables precise SOC estimation. The estimation process is further refined by integrating an extended Kalman filter (EKF) technique, along with open-circuit voltage computations. Simulation results demonstrate that this optimization strategy significantly improves SOC estimation accuracy, reducing the initial error to below 2.64% using the EKF approach, compared to a maximum battery model error of 3.88%. As a result, high performance is obtained from LIB packs.
Keywords
extended kalman filter
high-order equivalent model
Lithium-ion batteries
state of charge
parameter identification
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62373256, the Guangdong Basic and Applied Research Foundation under Grant 2024A1515013154 and the Science and Technology Development Foundation of the Shenzhen Government under Grant JCYJ20240813141419025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Monirul, I.M., Qiu, L., Ullah, I., Dashdondov, K., Khan, R.A., & Sharafian, A. (2025). A Novel Time-Variant State of Charge Estimation Based on an Extended Kalman Filtering Algorithm and Dynamic High-Order Modeling of Lithium-Ion Batteries. IECE Transactions on Power Electronics and Industrial Systems, 1(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.62762/TPEIS.2024.125048
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue