Abstract
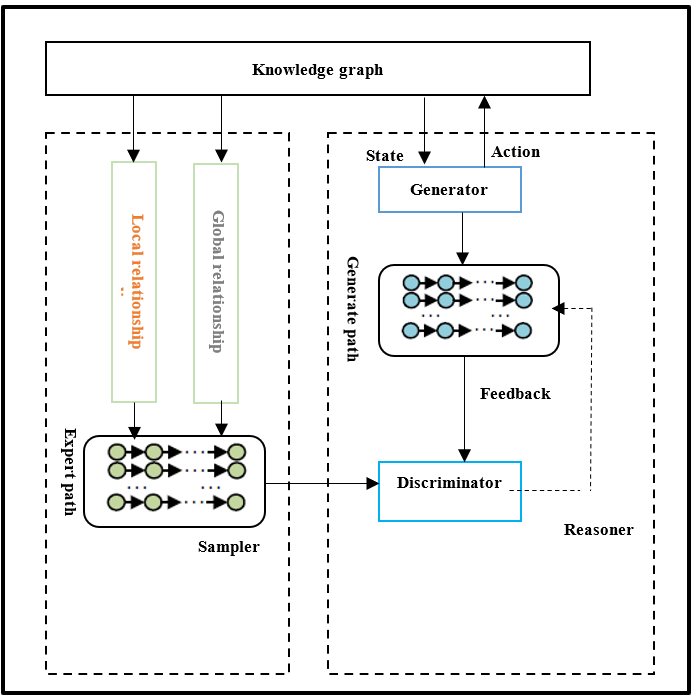
In the evolving framework of the Intelligence of Social Things (IoST), which amalgamates social networks and IoT ecosystems, knowledge graphs are essential for facilitating networked systems to efficiently process and leverage intricate relational data. Knowledge graphs offer essential technical assistance for various artificial intelligence applications, such as e-commerce, intelligent navigation, healthcare, and social media. Nonetheless, current knowledge graphs frequently lack completeness, harboring a considerable quantity of implicit knowledge that remains to be revealed. Consequently, tackling the difficulty of finalising knowledge graphs has emerged as a pressing research priority. Most contemporary methods separately analyse entity neighbourhood information or connection routes, neglecting the significance of entity neighbourhood information in the investigation of relationship paths. A novel approach, RPEN-KGC (Relationship Path and Entity Neighbourhood Knowledge Graph Completion), is suggested to enable the fusion of relationship paths and entity neighbourhood information for knowledge graph completion. RPEN-KGC comprises a sampler and an inferencer. The sampler conducts random walks between entity pairs to furnish dependable inference methods for the inferencer. The sampler utilises a contrastive method grounded in entity neighbourhood similarity to steer random walks, hence enhancing sampling efficiency and augmenting inference strategies. The inferencer derives semantic characteristics of relationship paths and deduces a greater variety of relationship paths within the semantic domain. Experiments performed on the public NELL-995 and FB15K-237 datasets for the link prediction task indicate that RPEN-KGC significantly enhances most metrics relative to baseline approaches. These findings demonstrate that RPEN-KGC proficiently forecasts absent information in knowledge graphs.
Keywords
intelligence of social things
artificial intelligence
knowledge graph
relationship path
entity neighborhood information
graph completion
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Shabaz, M., & Soni, M. (2025). Integrating Relationship Path and Entity Neighbourhood Information for Knowledge Graph Intelligence of Social Things. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion, 2(1), 27–37. https://doi.org/10.62762/CJIF.2025.197460
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 