Abstract
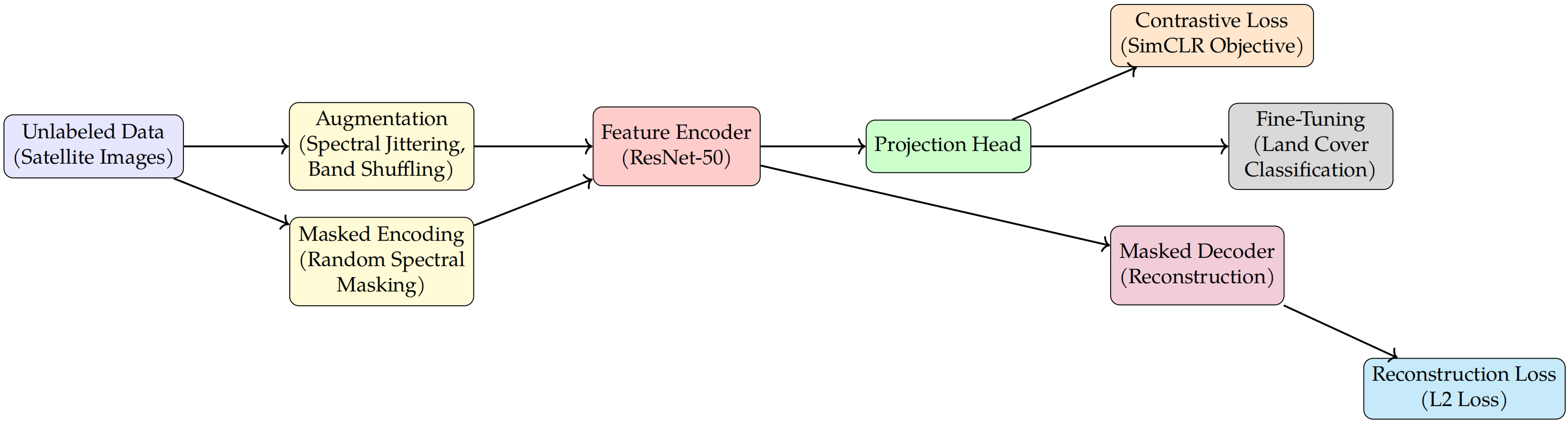
The scalability of modern AI is fundamentally limited by the availability of labeled data. While supervised learning achieves remarkable performance, it relies on large annotated datasets, which are expensive and time-consuming to acquire. This work explores self-supervised learning (SSL) as a promising solution to this challenge, enabling AI to scale effectively in data-scarce scenarios. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed SSL framework using the EuroSAT dataset, a benchmark for land cover classification where labeled data is limited and costly. The proposed approach integrates contrastive learning with multi-spectral augmentations, such as spectral jittering and band shuffling, along with masked autoencoding that applies spatial-spectral masking based on local variance in spectral bands. This method effectively captures the unique spatial and spectral characteristics of EuroSAT imagery. Experimental results show that the proposed SSL-based models achieve 81.2% accuracy with only 10% of the labeled data, outperforming supervised learning by 2.7% and semi-supervised methods by 2.1%. These results demonstrate the potential of SSL to reduce reliance on labeled data and enable effective AI deployment in data-constrained environments. The proposed work highlights the transformative potential of SSL in reducing annotation burdens, paving the way for more scalable, accessible, and cost-effective AI solutions.
Keywords
self-supervised Learning (SSL)
limited labeled data
data-scarce scenarios
contrastive learning
masked autoencoding
scalable AI
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Myakala, P.K. (2025). Scaling AI with Limited Labeled Data: A Self-Supervised Learning Approach. IECE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence, 2(1), 26–35. https://doi.org/10.62762/TETAI.2025.607708
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue