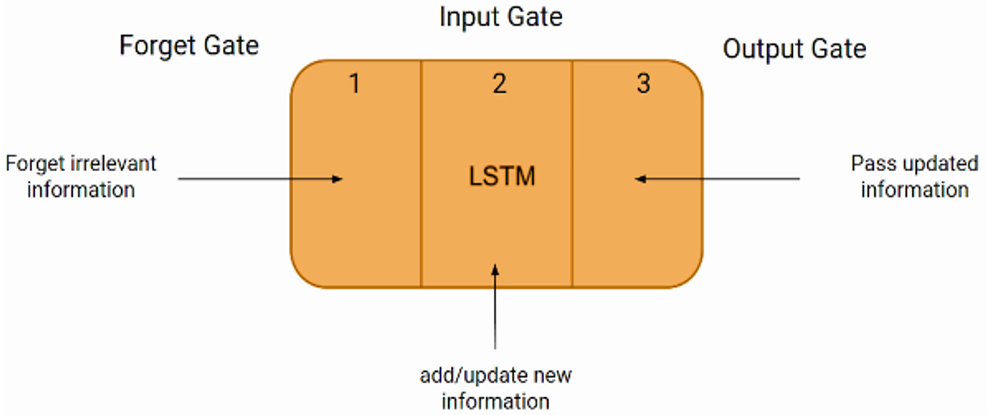
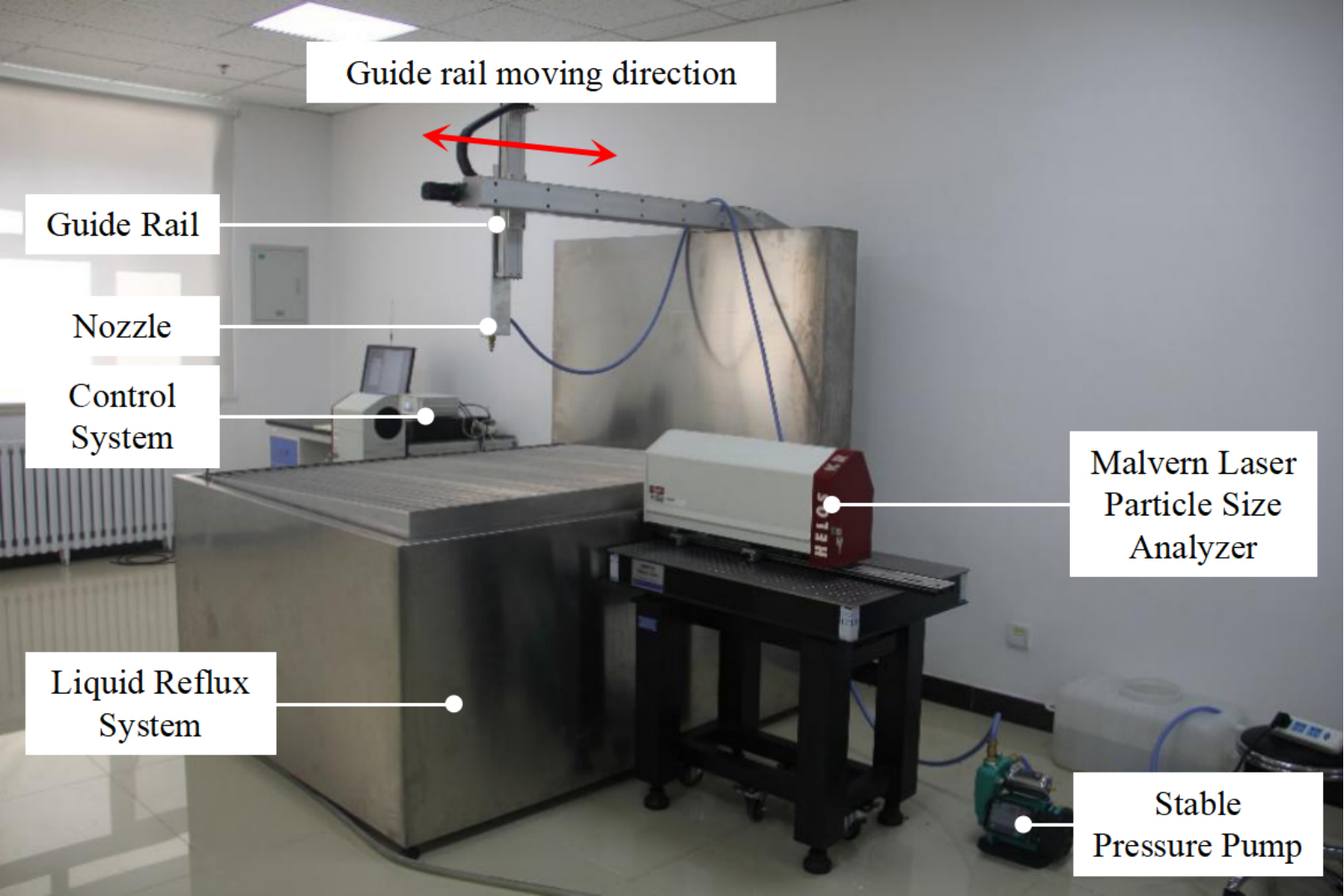
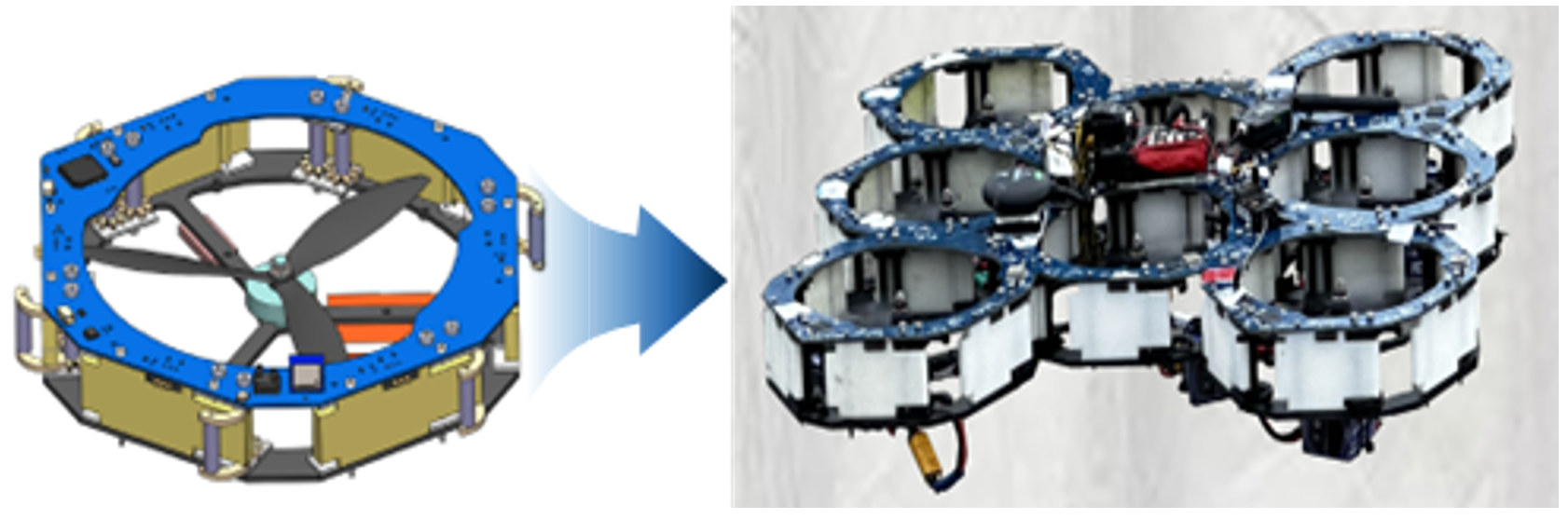
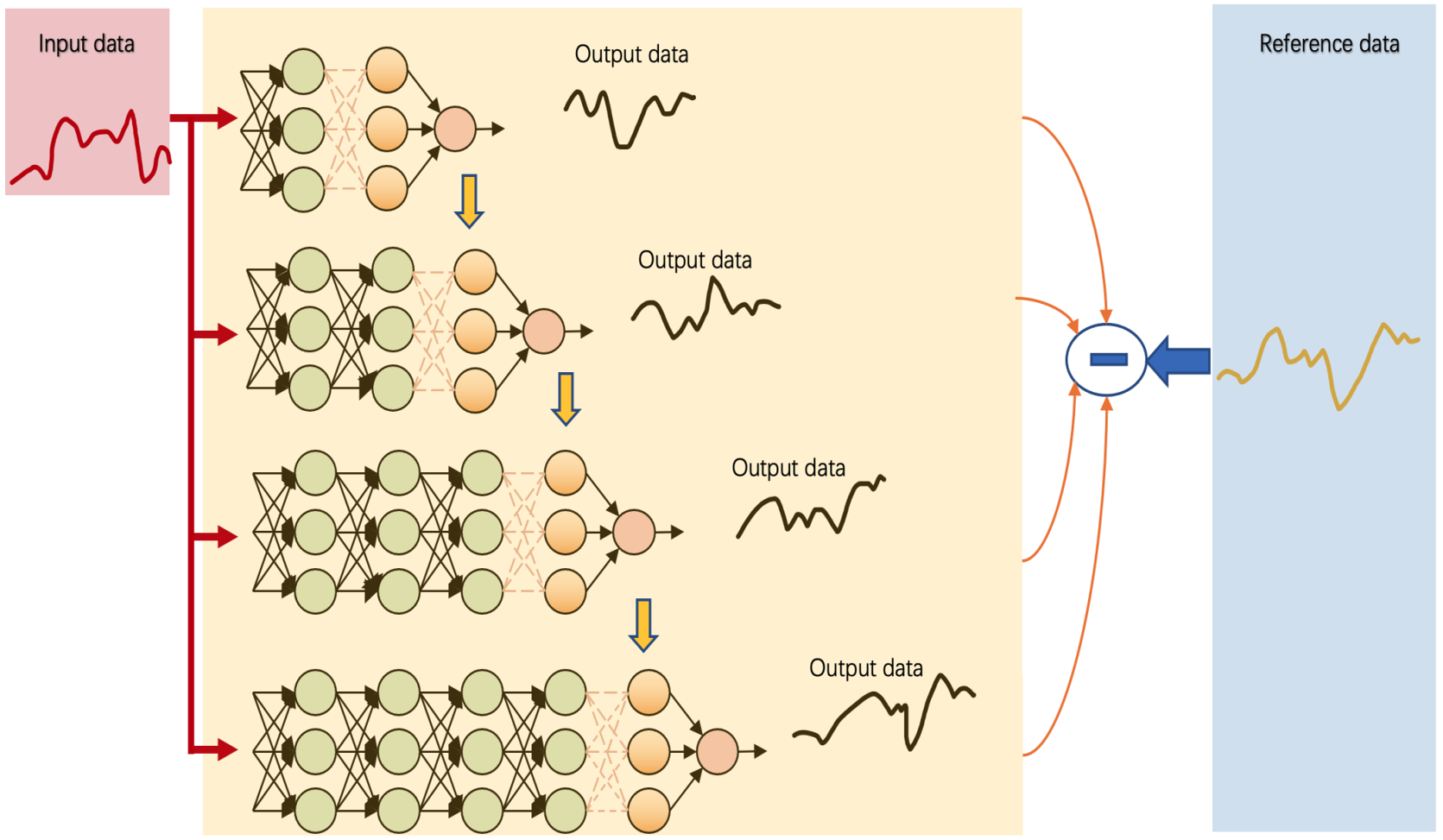
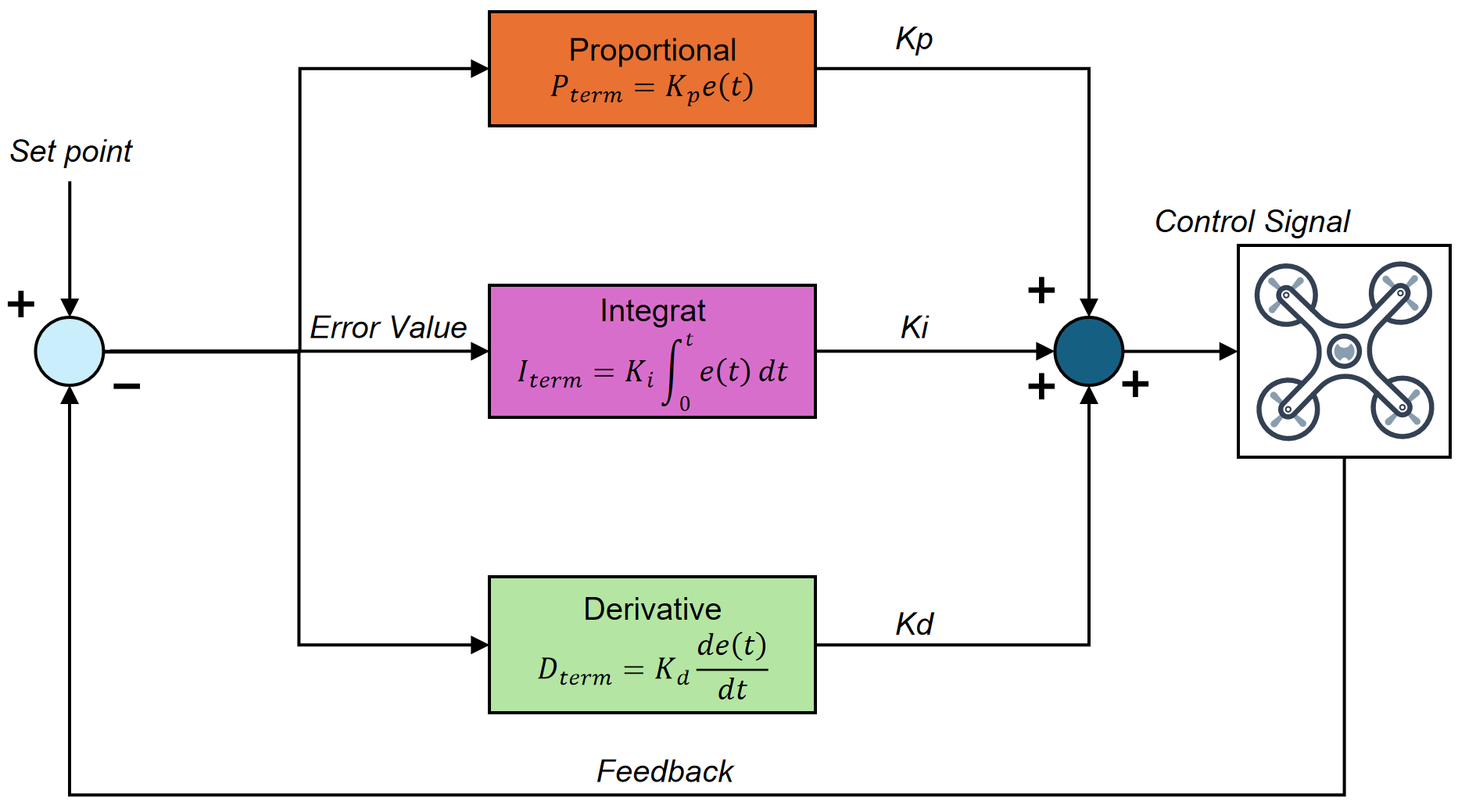
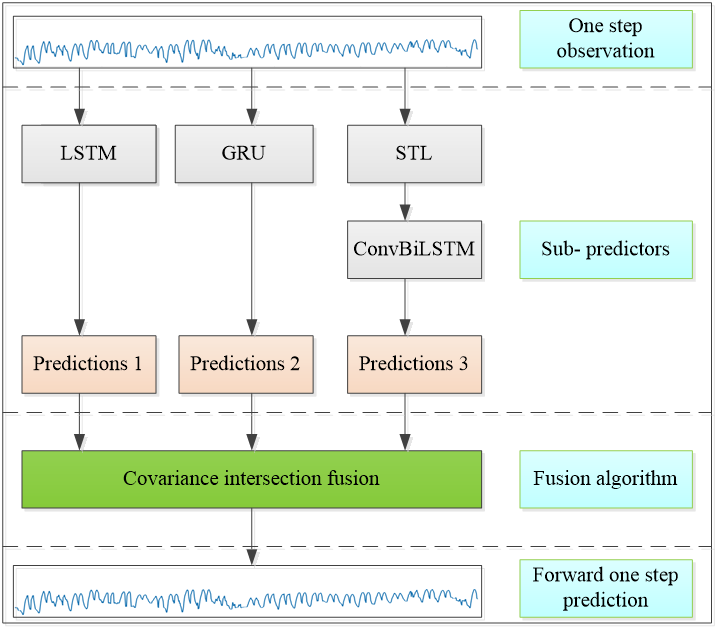
IECE Transactions on Intelligent Systematics | Volume 2, Issue 1: 66-75, 2025 | DOI:10.62762/TIS.2025.790920
Abstract
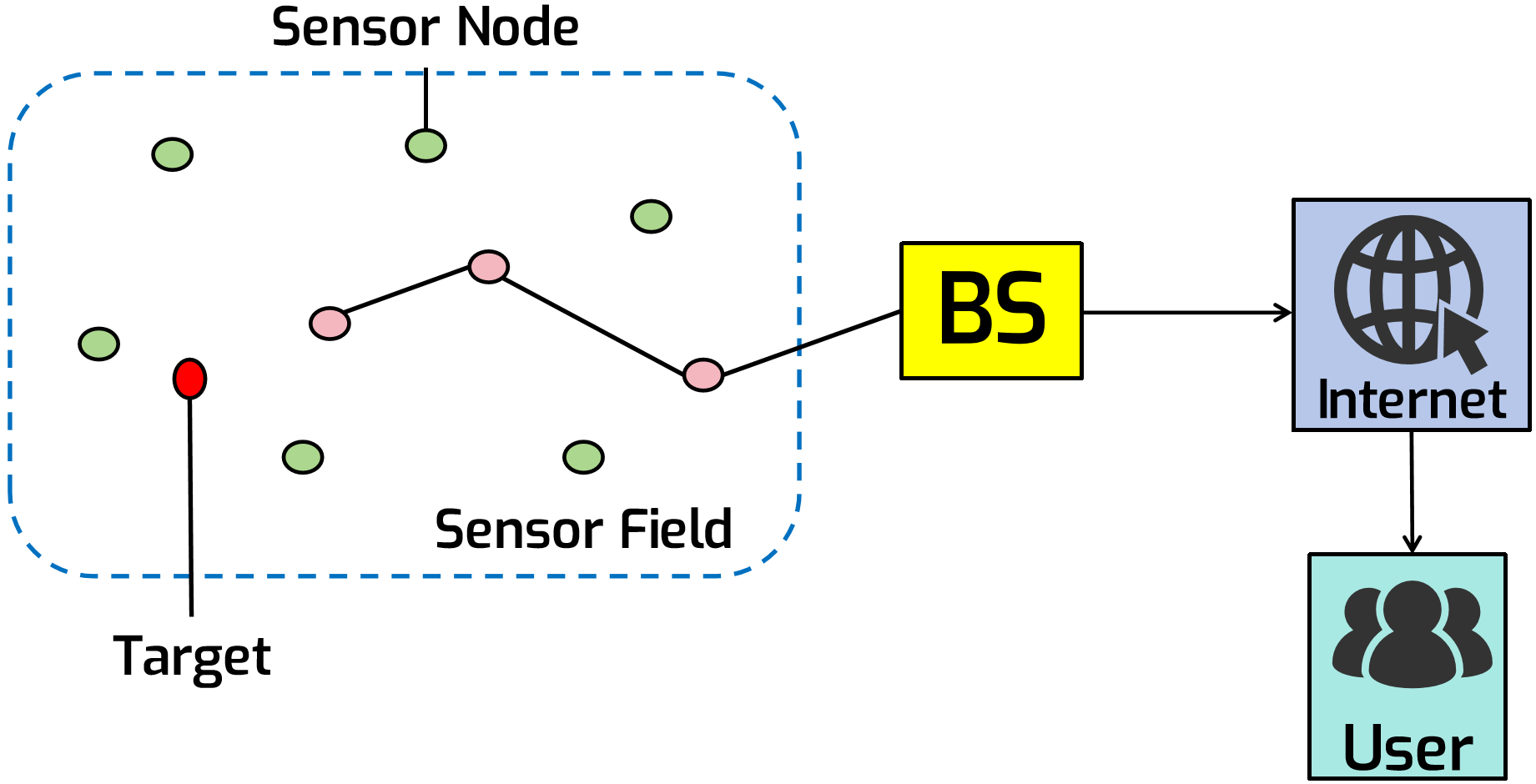
In the recent era of communication, wireless sensor networks (WSNs) emerged as a demanding area of study due to their communication capacity especially in the application of Internet of things (IoT). As the breadth and range of networks expand quickly, it becomes necessary to sense, transmit, and interpret the massive amount of data in IoT devices. WSN becomes even more beneficial and popular among the researchers when it integrates with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to increase the life span and establish a reliable communication between itself and Network Control Centre in an efficient way. Memory problems and network data transmission processing times are also addressed by this integrat... More >
Graphical Abstract